What Are The Relative Humidity Limits Recommended For Residences
Many homeowners face a common, frustrating problem: uneven heating or cooling throughout their home. One room might be comfortably warm (or cool), while another feels noticeably different. Often, people immediately suspect their HVAC system is failing. While that's a possibility, a less obvious culprit could be incorrect relative humidity levels. Understanding and managing humidity is crucial for comfort, health, and even the longevity of your home. This article will guide you through diagnosing humidity-related heating and cooling issues and offer practical solutions you can tackle yourself.
Understanding Relative Humidity and Its Impact
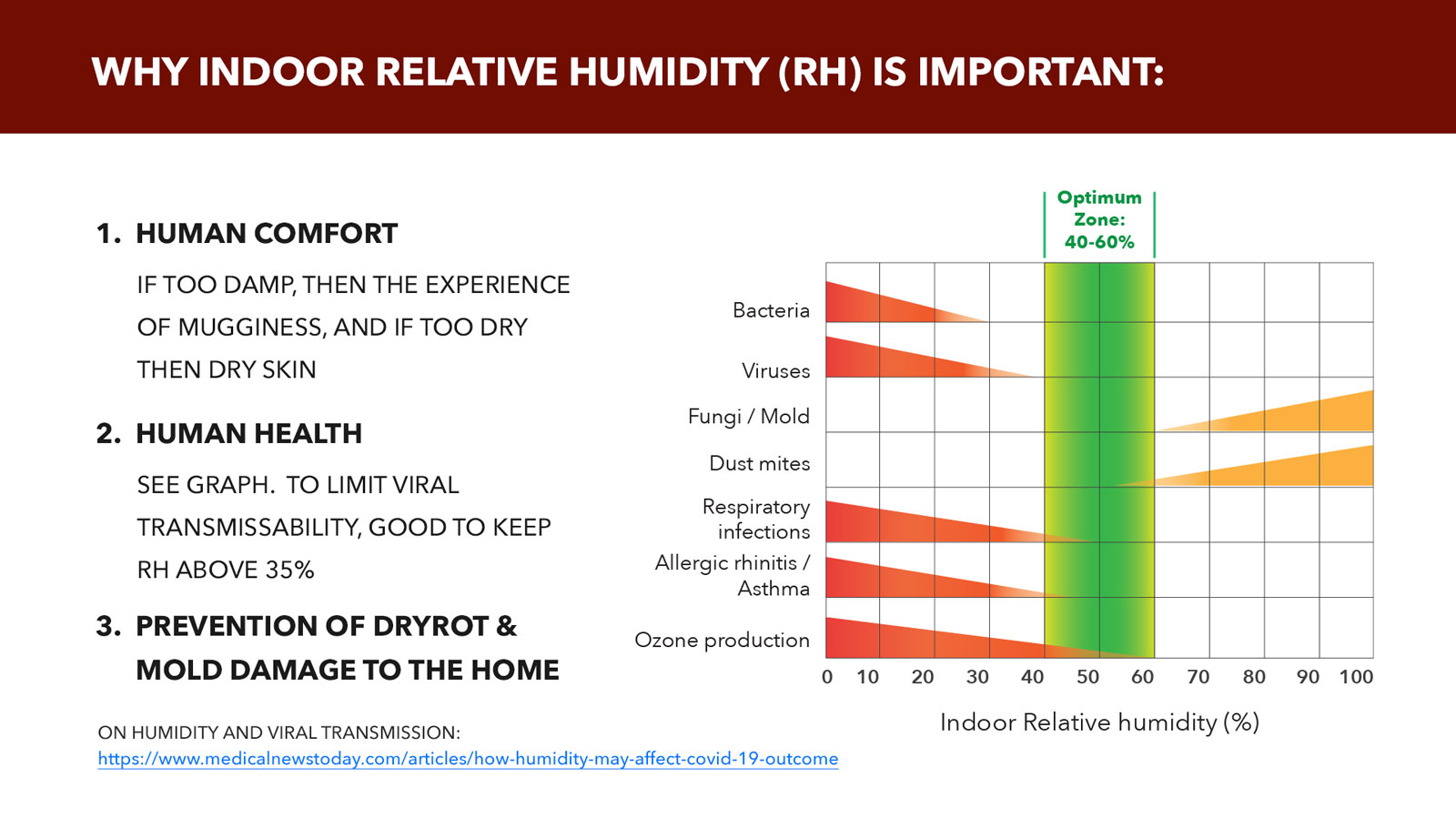
Relative humidity (RH) is the amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount the air could hold at a given temperature. It's expressed as a percentage. Think of it this way: 100% RH means the air is saturated and can't hold any more moisture (like a foggy day). Low RH means the air is very dry.
Why does RH matter? When RH is too high, the air feels hotter than it actually is because sweat doesn't evaporate effectively. This can lead to stuffiness, mold growth, and exacerbate respiratory problems. When RH is too low, the air feels colder, and can cause dry skin, irritated sinuses, and even damage wooden furniture. Maintaining the right RH balance is key to a comfortable and healthy home environment.
The recommended RH range for homes is generally between 30% and 50%. In the winter, you might aim for the lower end of that range to prevent condensation on windows. In the summer, the higher end can be more comfortable. Keeping humidity within these limits not only impacts comfort, but also helps prevent issues such as mold, wood rot, and damage to electronics.
Diagnosing Humidity-Related Heating and Cooling Problems
Before calling an HVAC technician, let's investigate if humidity is the root cause of your discomfort. Here's a methodical approach:
Step 1: Observe and Document
Start by carefully observing and documenting the symptoms you're experiencing. Consider these questions:
- Which rooms feel too hot or too cold?
- When do you notice the problem most acutely (day, night, specific weather conditions)?
- Are there any visible signs of moisture (condensation on windows, damp spots on walls, musty odors)?
- Do you or anyone in your household experience symptoms like dry skin, irritated sinuses, or increased allergy symptoms?
These observations provide valuable clues for identifying the issue and tracking the effectiveness of your solutions.
Step 2: Check Your Thermostat Settings
This might seem obvious, but double-check that your thermostat is set correctly for both heating and cooling. Make sure it's not in "fan only" mode, which can circulate air without actually heating or cooling it. Also, ensure the thermostat's location isn't compromised by direct sunlight or drafts, which can cause inaccurate readings. If you have a smart thermostat, ensure it’s properly calibrated and connected.
Without Tools: Visually inspect the thermostat display and settings. Manually adjust the temperature up or down a few degrees to see if the system responds.
Step 3: Measure Relative Humidity
To accurately assess the humidity level, you'll need a hygrometer (also called a humidity meter). These are inexpensive and readily available at most hardware stores or online retailers. Place the hygrometer in different rooms, especially those where you're experiencing discomfort. Give it some time (usually 15-30 minutes) to provide an accurate reading. Record the RH levels in each room.
Requires Basic Equipment: A hygrometer is essential for this step.
Step 4: Inspect for Obvious Moisture Sources
Look for potential sources of excess moisture inside your home. These could include:
- Leaky pipes or faucets: Check under sinks, around toilets, and in the basement for any signs of water leaks.
- Poorly ventilated bathrooms: Ensure exhaust fans are working properly and used during and after showers or baths.
- Clothes dryers: Make sure the dryer vent is properly connected and venting to the outside. A blocked or disconnected vent can release significant moisture into your home.
- Cooking: Boiling water or using a dishwasher can increase humidity levels.
- Basement/crawlspace issues: Check for signs of dampness, water intrusion, or inadequate ventilation.
Without Tools: Visually inspect for leaks, condensation, and proper ventilation. Sniff for musty odors, which can indicate mold growth.
Step 5: Assess Your Home's Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is crucial for controlling humidity. Stale, moist air needs to be exchanged with fresh, drier air. Check the following:
- Attic ventilation: Ensure vents are not blocked by insulation or debris. Proper attic ventilation helps prevent moisture buildup and ice dams in the winter.
- Crawlspace ventilation: If you have a crawlspace, make sure it has adequate ventilation to prevent moisture from seeping into your home.
- General airflow: Are there any areas in your home that feel stagnant or stuffy? Improving airflow can help reduce humidity levels.
Without Tools: Visually inspect vents for blockages. Observe the general airflow in different rooms. A stuffy or stagnant feeling may indicate poor ventilation.
DIY Actions to Improve Relative Humidity
Once you've identified potential causes, you can take several DIY steps to improve your home's relative humidity. Always prioritize safety when working with electrical appliances or water sources.
Addressing High Humidity
If your RH readings are consistently above 50%, focus on these solutions:
- Increase Ventilation: Open windows when the weather permits (when the outside humidity is lower than inside). Use exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens to remove moisture. Consider installing a whole-house fan to improve overall ventilation.
- Fix Leaks: Repair any leaky pipes or faucets promptly. Even small drips can contribute to significant moisture buildup over time.
- Ensure Proper Dryer Venting: Check your dryer vent to make sure it's properly connected and venting to the outside. Clean the vent regularly to remove lint buildup, which can restrict airflow and increase moisture levels.
- Use a Dehumidifier: A dehumidifier removes excess moisture from the air. Choose a model that's appropriately sized for the room or area you want to dehumidify. Empty the water reservoir regularly.
- Improve Air Circulation: Use fans (ceiling fans, portable fans) to circulate air, especially in stagnant areas. This helps to evaporate moisture and prevent mold growth.
- Manage Indoor Plants: While plants can be beneficial, too many indoor plants can increase humidity levels. Consider reducing the number of plants in your home or moving them to a well-ventilated area.
- Address Basement/Crawlspace Moisture: If you have a damp basement or crawlspace, consider installing a vapor barrier or a dehumidifier. Ensure proper drainage around your foundation to prevent water from seeping into these areas.
Addressing Low Humidity
If your RH readings are consistently below 30%, consider these actions:
- Use a Humidifier: A humidifier adds moisture to the air. There are several types of humidifiers available, including whole-house humidifiers, console humidifiers, and personal humidifiers. Choose a model that's appropriate for your needs and clean it regularly to prevent mold and bacteria growth.
- Reduce the Use of Exhaust Fans: Limit the use of exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens, as they can remove moisture from the air.
- Air Dry Laundry Indoors: Hanging clothes to dry indoors can add moisture to the air. However, be mindful of potential mold growth if the air is not well-ventilated.
- Add Indoor Plants: Certain plants can help increase humidity levels in your home. Choose plants that are known for their moisture-releasing properties.
- Boil Water or Simmer on the Stove: Leaving a pot of water to simmer on the stove can add moisture to the air. Be sure to monitor the water level and refill as needed.
When to Call a Professional HVAC Technician
While many humidity-related issues can be resolved with DIY solutions, some situations require the expertise of a qualified HVAC technician. Call a professional if:
- You suspect a refrigerant leak: Refrigerant leaks can affect your system's ability to dehumidify the air. This requires specialized equipment to detect and repair.
- Your HVAC system is old or malfunctioning: An aging or malfunctioning HVAC system may not be able to effectively control humidity levels. A technician can diagnose and repair or replace your system.
- You have mold growth that you can't easily remove: Extensive mold growth indicates a serious moisture problem that requires professional remediation.
- You've tried DIY solutions without success: If you've implemented DIY solutions and your humidity problems persist, it's time to consult a professional.
- You're uncomfortable working with electrical or plumbing systems: Safety should always be your top priority. If you're not comfortable working with electrical or plumbing systems, leave it to the professionals.
Attempting repairs you're not qualified for can be dangerous and may void your warranty. When in doubt, always consult a professional.
Maintenance Tips for Maintaining Optimal Humidity Levels
Preventative maintenance is key to keeping your home's humidity levels in check. Consider these tips:
- Regularly inspect and maintain your HVAC system: Schedule regular maintenance checks with a qualified HVAC technician to ensure your system is running efficiently.
- Clean or replace air filters regularly: Dirty air filters can restrict airflow and affect your system's ability to control humidity.
- Ensure proper insulation: Adequate insulation helps to maintain consistent temperatures and prevent condensation.
- Monitor humidity levels regularly: Use a hygrometer to monitor humidity levels in different rooms and make adjustments as needed.
- Address any water leaks promptly: Repair any leaks as soon as you notice them to prevent moisture buildup.
- Maintain proper ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in your home to remove excess moisture and prevent mold growth.
By following these tips, you can create a comfortable, healthy, and energy-efficient home environment.

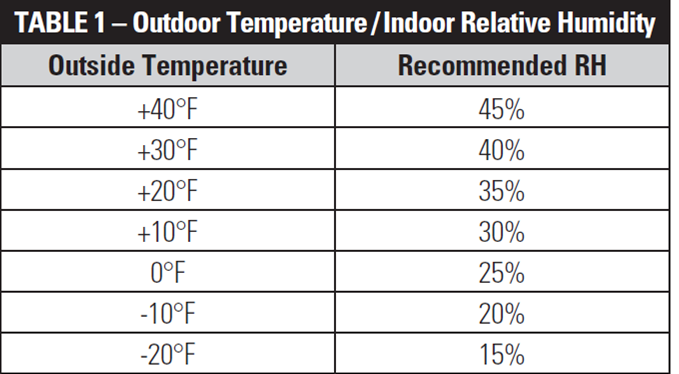
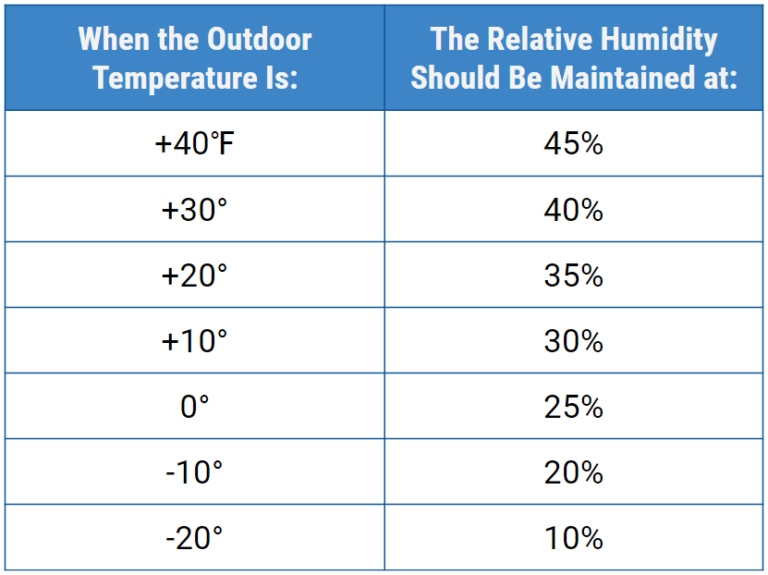

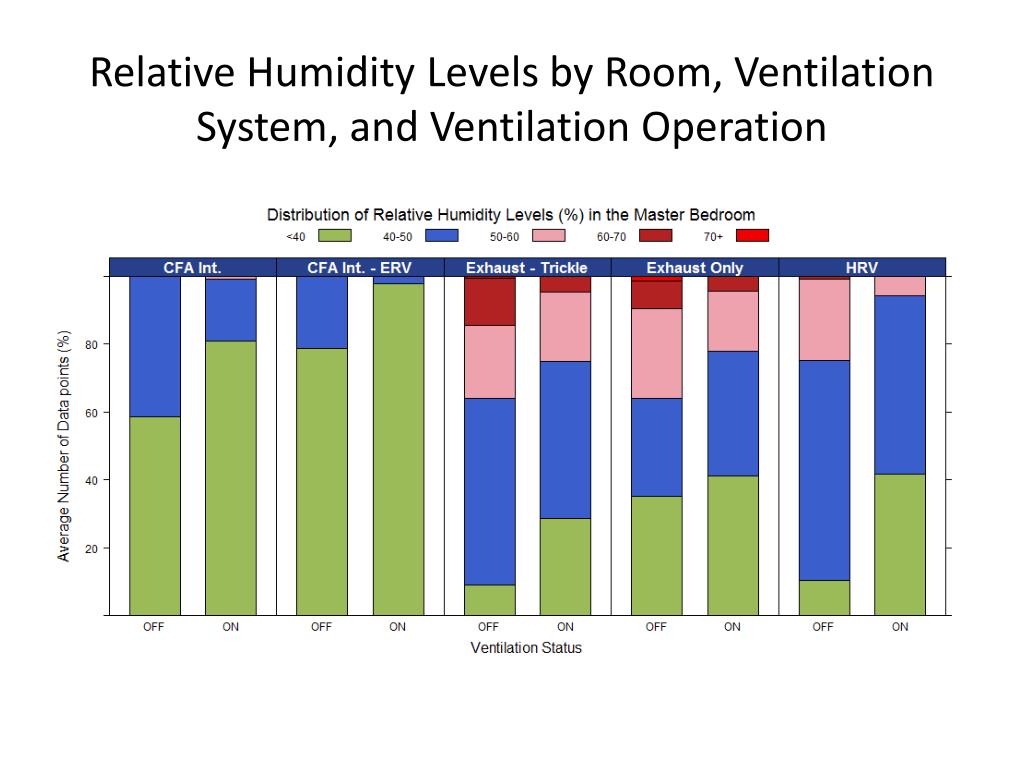

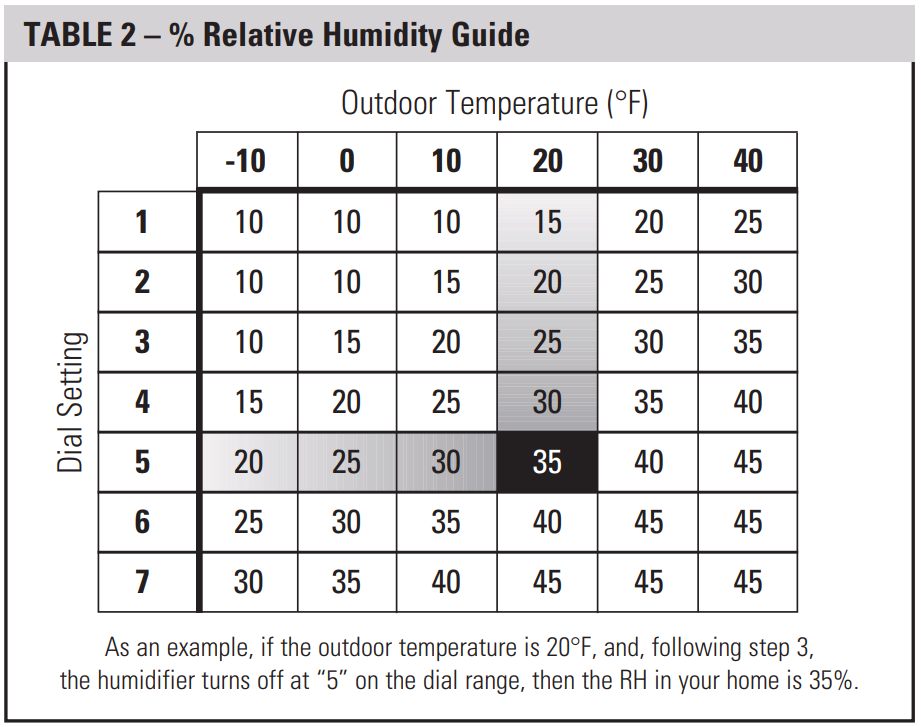
.jpg?width=1754&name=Humidity level chart (1).jpg)


