What Does A Boiler Do In A House

Understanding the role of a boiler in your home is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and efficient living environment. Boilers are a popular heating solution, especially in colder climates. This guide will explain what a boiler does, how it works, and the different types available, helping you make informed decisions about your home heating system.
What Exactly Does a Boiler Do?
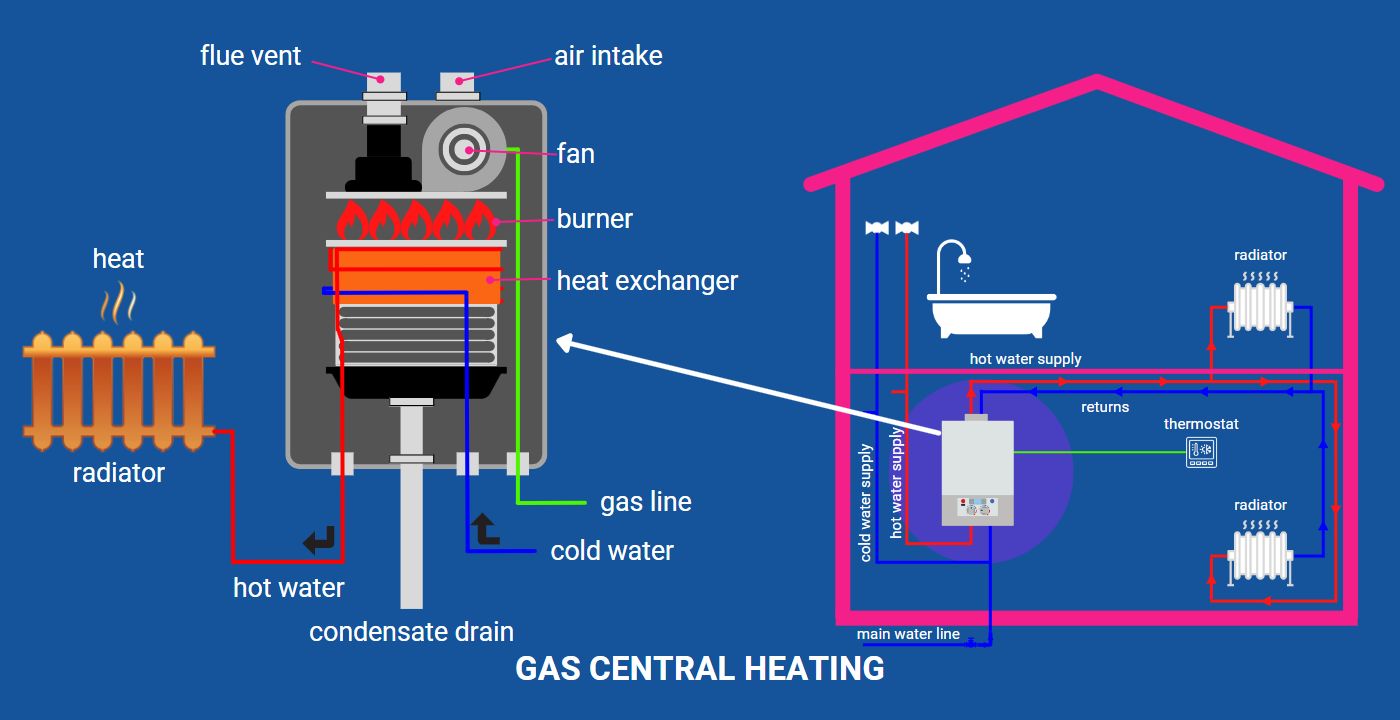
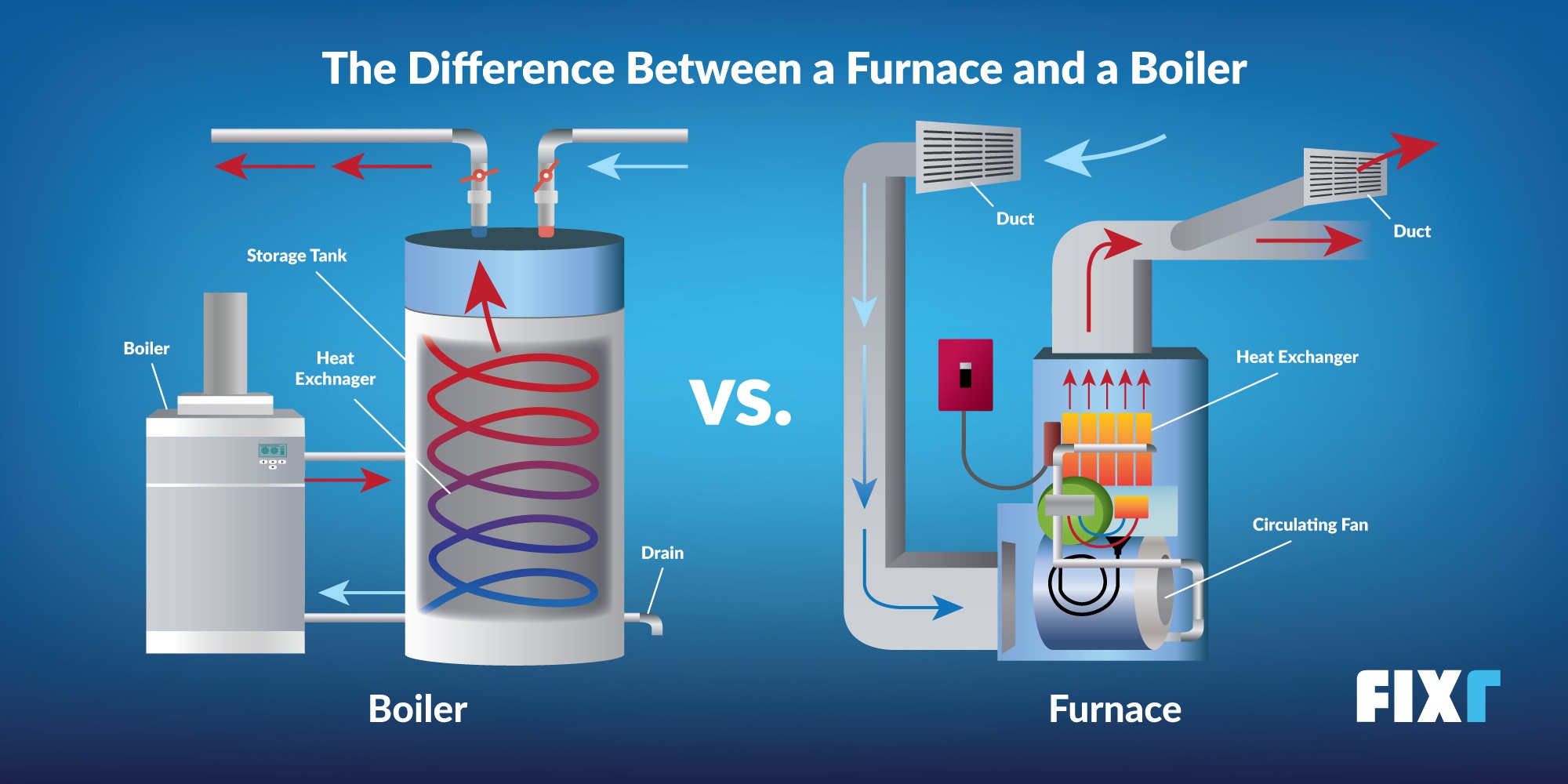
At its core, a boiler's primary function is to heat water. This heated water is then used to provide warmth throughout your home. Unlike a furnace, which heats air, a boiler heats water, which is then circulated to radiators, baseboard heaters, or radiant floor systems.
Think of it like this: imagine boiling water in a kettle. Instead of just making tea, the hot water produced by a boiler is sent through pipes to various points in your house, distributing warmth efficiently. This makes boilers a reliable and effective heating solution for many homes.
How Does a Boiler Work? A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The process of a boiler heating your home involves several key steps:
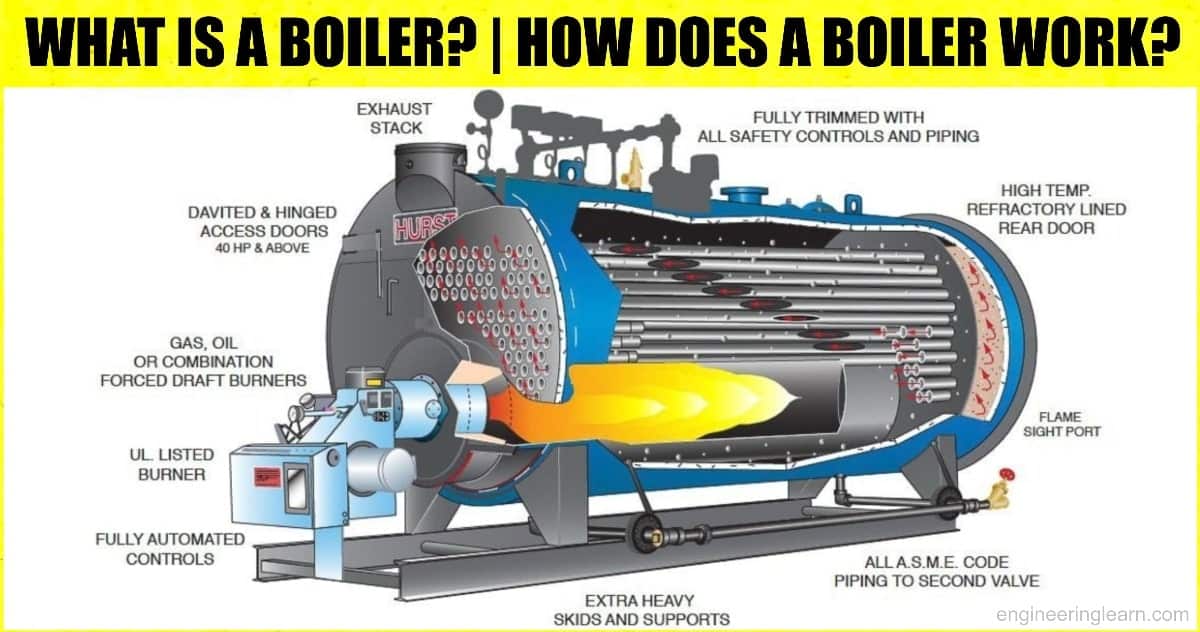
1. Combustion: Creating the Heat
The initial step involves combustion. Boilers typically burn fuel, such as natural gas, propane, or oil, inside a combustion chamber. Some modern boilers use electricity instead of fuel. This combustion process generates a significant amount of heat.
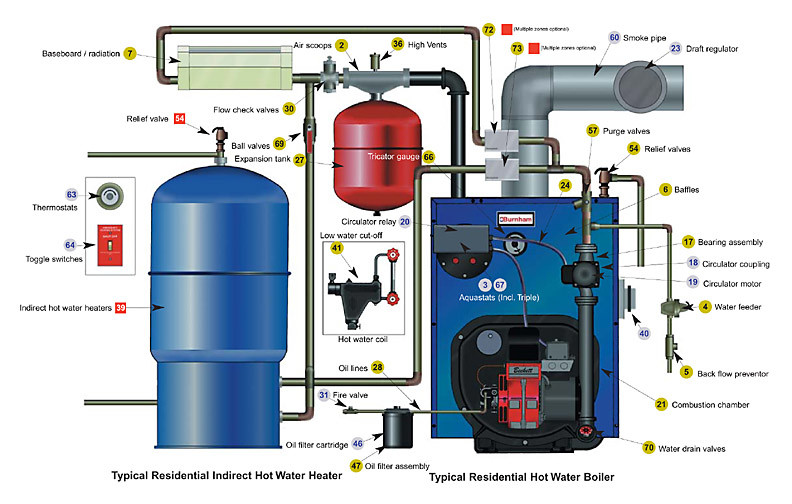
2. Heat Exchanger: Transferring the Heat
The heat generated from combustion is then transferred to water through a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger is a crucial component, usually made of metal, that allows the heat from the combustion gases to efficiently warm the water without the water and exhaust gases directly mixing. This maximizes efficiency and safety.
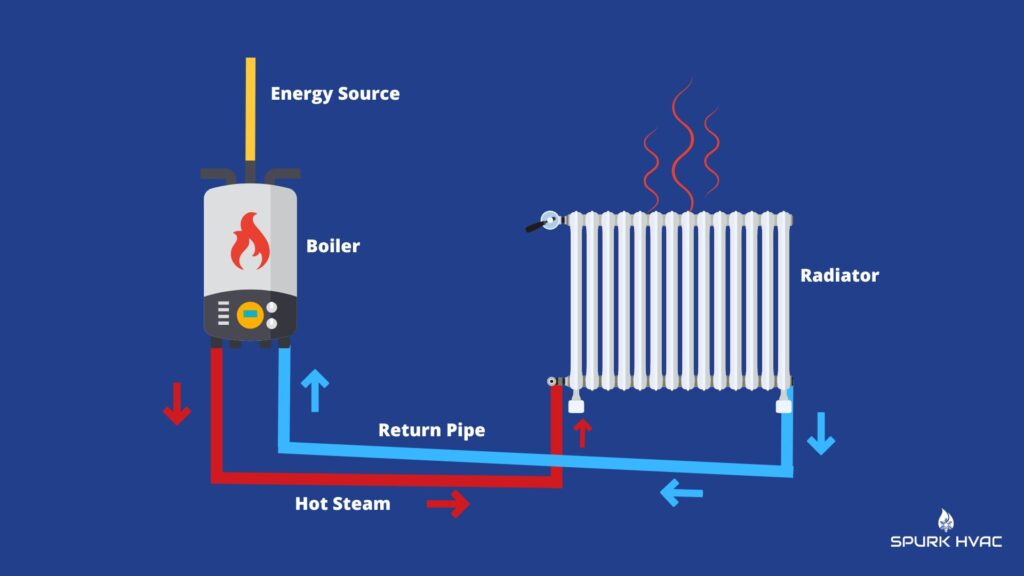
3. Water Circulation: Delivering the Warmth
Once the water is heated, it's circulated throughout your home via a network of pipes. A circulator pump pushes the hot water through these pipes to radiators, baseboard heaters, or radiant floor systems. These components then radiate heat into the surrounding rooms, effectively warming your living space.
4. Condensation (in High-Efficiency Boilers): Maximizing Efficiency
Many modern boilers are high-efficiency condensing boilers. These boilers have an additional step: they capture the heat from the exhaust gases that would normally be wasted. They do this by condensing the water vapor in the exhaust gases. This process releases latent heat, which is then used to further heat the water. This significantly improves the boiler's efficiency.
5. Return Cycle: Completing the Loop
After the hot water has circulated through the heating system and released its heat, it returns to the boiler to be reheated. This closed-loop system ensures a continuous supply of heat to your home.
Types of Boilers: Choosing the Right Option
Boilers come in various types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is important for selecting the right boiler for your specific needs.
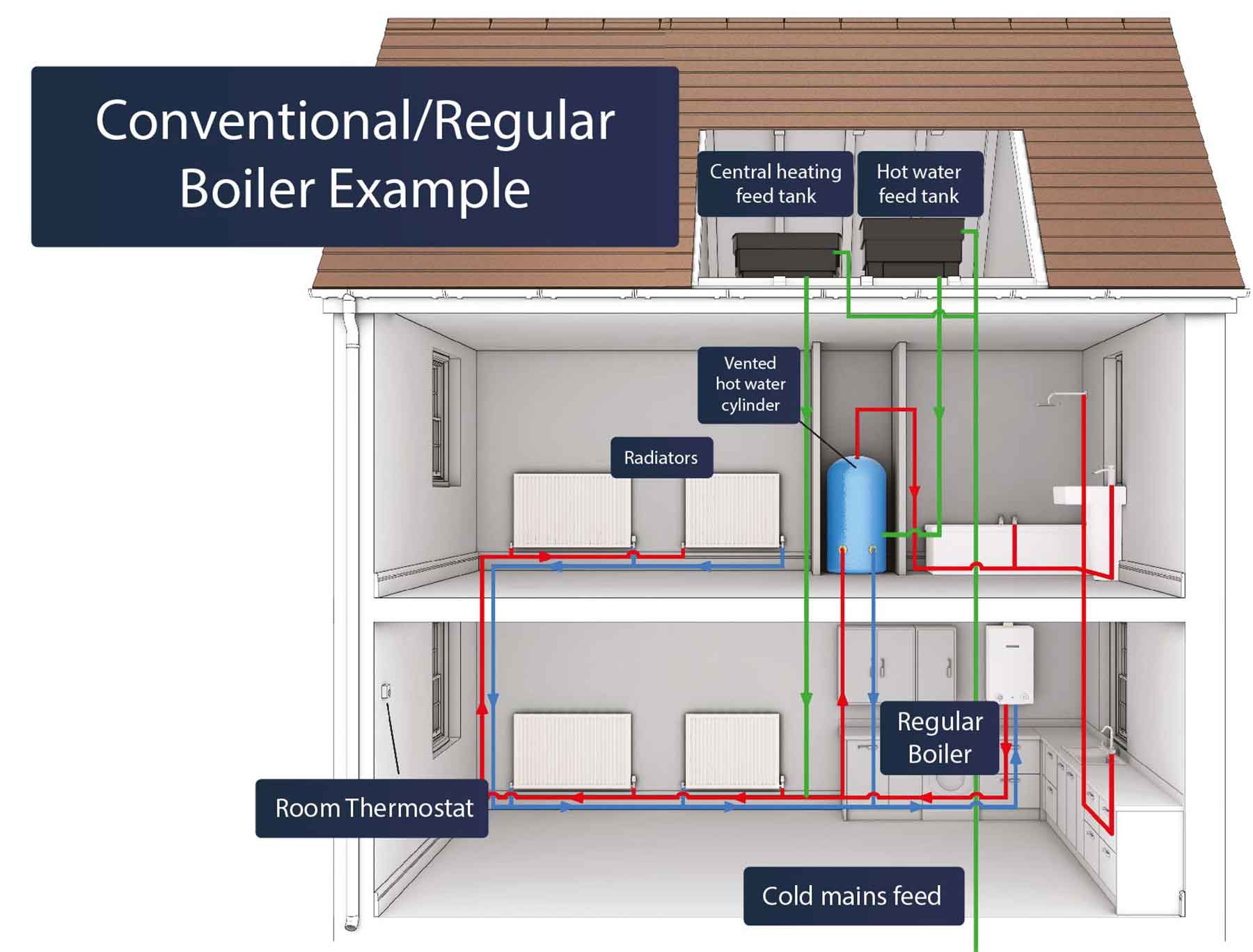
1. Conventional Boilers (Regular or Heat-Only)
These are the traditional type of boiler. They require a separate hot water cylinder to store hot water for domestic use (showers, sinks, etc.). They are generally less efficient than newer condensing boilers. They operate by heating water and sending it to radiators or a hot water storage tank.
2. Combi Boilers (Combination Boilers)
Combi boilers are a popular choice as they provide both central heating and hot water on demand, without the need for a separate hot water cylinder. This makes them ideal for smaller homes with limited space. They are generally more efficient than conventional boilers because they only heat water when needed, reducing standby heat losses. When a hot water tap is turned on, the combi boiler instantly diverts hot water to the tap instead of the central heating system. This makes them highly convenient.
3. System Boilers
System boilers are similar to conventional boilers in that they work with a hot water cylinder. However, unlike conventional boilers, many of the components, such as the pump and expansion vessel, are built into the boiler itself. This makes installation easier and neater. They are well-suited for homes with higher hot water demands, such as those with multiple bathrooms.
4. Condensing Boilers
As mentioned earlier, condensing boilers are highly efficient. They recover heat from the exhaust gases that would normally be wasted. This can significantly reduce your energy bills. They are available in combi, system, and conventional configurations. Due to their high efficiency, many governments offer incentives or rebates for installing condensing boilers.
5. Electric Boilers
Electric boilers use electricity to heat water. They are generally smaller and quieter than gas or oil boilers and do not require a flue (vent). However, they can be more expensive to operate, especially in areas with high electricity costs. They are a good option for homes without access to natural gas or propane.
Benefits of Using a Boiler for Home Heating
Boilers offer several advantages over other heating systems, such as furnaces:
- Efficient Heating: Boilers, especially condensing models, can be highly efficient, converting a large percentage of fuel into usable heat.
- Consistent Temperature: Radiant heating systems, which are often used with boilers, provide a more consistent and even temperature throughout the home compared to forced-air systems.
- Quiet Operation: Boilers are generally quieter than furnaces. There's no noisy blower fan cycling on and off.
- Zoned Heating: Boilers can be easily integrated with zoned heating systems, allowing you to control the temperature in different areas of your home independently.
- Reduced Allergens: Radiant heating systems don't circulate dust and allergens like forced-air systems, making them a good choice for people with allergies or asthma.
Potential Drawbacks of Boilers
While boilers offer many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Installation Costs: The initial cost of installing a boiler can be higher than that of a furnace.
- Maintenance: Boilers require regular maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently and safely. This may include annual inspections and cleaning.
- Repair Costs: Boiler repairs can sometimes be expensive, especially if major components need to be replaced.
- Slower Response Time: Radiant heating systems can take longer to heat up a room compared to forced-air systems.
- Potential for Leaks: Because they use water, there's always a potential for leaks. Regular inspection is important to prevent water damage.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Boiler
Selecting the right boiler for your home depends on several factors:
- Size of Your Home: The size of your home will determine the required heating capacity of the boiler. A larger home will require a more powerful boiler.
- Climate: The climate in your area will also influence the required heating capacity. Colder climates will require a more powerful boiler.
- Fuel Type: Consider the availability and cost of different fuel types in your area (natural gas, propane, oil, electricity).
- Efficiency: Choose a boiler with a high efficiency rating to minimize your energy bills. Look for the AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) rating. The higher the AFUE, the more efficient the boiler.
- Budget: Set a budget for the purchase and installation of the boiler, taking into account both the initial cost and the long-term operating costs.
- Hot Water Needs: Consider your hot water needs. If you have a large family or frequently use multiple hot water appliances at the same time, a combi boiler may not be sufficient. A system boiler with a hot water cylinder may be a better option.
Maintenance Tips for Your Boiler
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your boiler running efficiently and safely. Here are some tips:
- Annual Inspection: Schedule an annual inspection by a qualified HVAC technician.
- Bleed Radiators: Bleed your radiators regularly to remove trapped air, which can reduce their efficiency.
- Check Water Pressure: Monitor the water pressure in your boiler system and maintain it at the recommended level.
- Clean the Boiler: Clean the boiler and its components regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Replace Air Filters: If your boiler has air filters, replace them regularly to ensure proper airflow.
- Inspect Flue: Regularly inspect the flue (vent) for any signs of damage or blockage.
In Conclusion
A boiler is a vital component of many homes, providing efficient and reliable heating. By understanding how a boiler works, the different types available, and the benefits and drawbacks of using a boiler, you can make an informed decision about the best heating solution for your home. Remember to consider factors such as the size of your home, your climate, your fuel options, and your budget. Regular maintenance is also crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your boiler system. Investing in a high-quality boiler and properly maintaining it will provide years of comfortable and cost-effective heating for your home.