What Does Btu On An Air Conditioner Mean
Understanding the capacity of your air conditioner is crucial for maximizing its efficiency and minimizing energy costs. One of the most important measurements to grasp is BTU, or British Thermal Unit. But what does BTU on an air conditioner *really* mean, and how does it affect your wallet and the environment? This article breaks down the BTU rating, explaining its significance for homeowners, businesses, and anyone looking to make informed decisions about their HVAC systems.
Decoding BTU: A Simple Explanation
Simply put, a BTU (British Thermal Unit) is a unit of measurement for heat. Specifically, it's the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. In the context of air conditioning, BTU ratings indicate how much heat an air conditioner can remove from a room in one hour. So, an air conditioner with a 12,000 BTU rating can remove 12,000 BTUs of heat per hour.
It's crucial to understand that a higher BTU rating doesn't automatically mean "better." In fact, an oversized air conditioner can be just as inefficient as an undersized one. The goal is to choose an air conditioner with a BTU rating that's appropriately sized for the space you're trying to cool.
The Importance of Proper Sizing
Why is sizing so critical? Let's explore the consequences of both undersized and oversized air conditioners:
- Undersized Air Conditioner: An undersized unit will struggle to cool the space, especially during peak summer heat. It will run constantly, consuming more energy than necessary, and may never reach the desired temperature. This leads to higher energy bills and a shorter lifespan for the unit.
- Oversized Air Conditioner: While it might seem logical to assume a larger unit is always better, an oversized air conditioner cycles on and off frequently. This short-cycling prevents it from properly dehumidifying the air, leading to a clammy and uncomfortable environment. Furthermore, frequent starting and stopping put extra strain on the components, reducing the unit's lifespan and increasing maintenance costs. Oversized units are also less energy-efficient because they don't run long enough to reach their optimal operating efficiency.
The ideal scenario is an air conditioner that runs for a sustained period, effectively cooling and dehumidifying the space without constantly cycling on and off. This maximizes energy efficiency and provides consistent comfort.
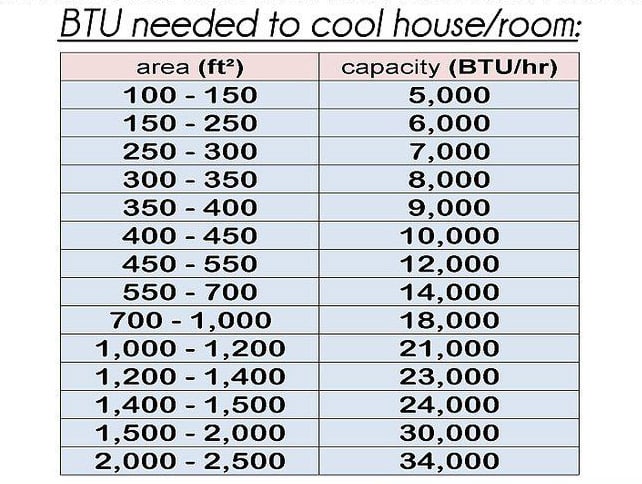
Calculating Your Cooling Needs: Finding the Right BTU Rating
Determining the correct BTU rating for your air conditioner is essential for optimal performance and energy savings. While there are several factors to consider, a general guideline is to use a BTU calculator or consult with an HVAC professional. Here are some key factors that influence the required BTU rating:
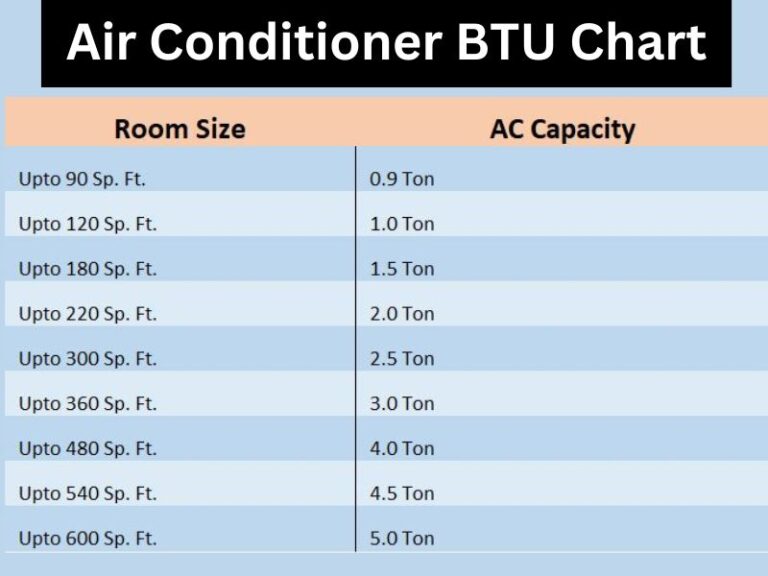
- Room Size: This is the most important factor. A larger room requires a higher BTU rating. A general rule of thumb is to start with 20 BTU per square foot of living space. For example, a 200 square foot room would need approximately 4,000 BTUs.
- Ceiling Height: Rooms with high ceilings require more cooling power.
- Climate: Hotter climates require higher BTU ratings.
- Insulation: Poor insulation allows heat to enter the room, requiring a higher BTU rating.
- Sun Exposure: Rooms with significant sun exposure need more cooling power.
- Number of Occupants: More people generate more heat.
- Heat-Generating Appliances: Appliances like computers and TVs generate heat, which must be accounted for.
Many online BTU calculators can provide a more accurate estimate based on these factors. However, it's always recommended to consult with a qualified HVAC technician for a professional assessment.
Example BTU Calculation
Let's say you have a living room that's 300 square feet, with standard 8-foot ceilings, moderate insulation, and faces east (moderate sun exposure). The climate is considered warm. Using the 20 BTU per square foot rule, you'd start with 6,000 BTU. However, considering the warm climate and moderate sun exposure, you might need to add another 1,000-2,000 BTU, bringing the total to 7,000-8,000 BTU. A professional assessment would provide a more precise recommendation.
Beyond BTU: Understanding SEER and EER
While BTU measures cooling capacity, SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) measure the energy efficiency of an air conditioner. Understanding these ratings is equally important for making an informed purchasing decision.
- SEER: SEER measures the overall cooling efficiency of an air conditioner over an entire cooling season. It's calculated by dividing the total cooling output (in BTU) during a typical cooling season by the total electrical energy input (in watt-hours) during the same period. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the air conditioner. The minimum SEER rating currently required in the United States is 14 for most central air conditioners. Energy Star certified units typically have even higher SEER ratings.
- EER: EER measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner under specific conditions: an outdoor temperature of 95°F and an indoor temperature of 80°F with 50% relative humidity. EER is calculated by dividing the cooling output (in BTU) by the electrical power input (in watts) at those specific conditions. While SEER provides a more comprehensive picture of seasonal efficiency, EER can be useful for comparing the efficiency of different models under standardized conditions.
When choosing an air conditioner, prioritize models with higher SEER and EER ratings to minimize energy consumption and save money on your utility bills. A unit with a higher SEER rating will use less electricity to provide the same amount of cooling as a unit with a lower SEER rating.
Energy Savings and ROI: Investing in Efficiency
Investing in an energy-efficient air conditioner with the appropriate BTU rating can result in significant long-term savings. While the initial cost may be higher, the reduced energy consumption will pay for itself over time. Here's how to calculate the potential ROI:
- Calculate Annual Cooling Costs: Determine your current annual cooling costs based on your electricity bills.
- Estimate Savings with a Higher SEER Unit: Compare the energy consumption of your existing unit with a higher SEER unit. Use online calculators or consult with an HVAC professional to estimate the annual savings.
- Factor in Rebates and Incentives: Check for available rebates and incentives from your local utility company or government agencies. Many programs offer financial assistance for purchasing energy-efficient appliances. Energy Star provides a comprehensive list of qualified products and available rebates.
- Calculate Payback Period: Divide the difference in cost between the new and old unit by the estimated annual savings (including rebates). This will give you the payback period, indicating how long it will take for the energy savings to offset the initial investment.
For example, upgrading from a SEER 10 unit to a SEER 16 unit could reduce your cooling costs by 37%. If your annual cooling costs are currently $500, you could save $185 per year. With rebates and incentives, the payback period could be as short as 3-5 years. After that, you'll be enjoying significant savings for the remaining lifespan of the air conditioner.
Smart HVAC Integration: Optimizing Performance with Technology
Integrating your air conditioner with smart home technology can further enhance its efficiency and performance. Smart thermostats, sensors, and automated controls allow you to optimize cooling based on occupancy, weather conditions, and your personal preferences.
- Smart Thermostats: Learn your heating and cooling patterns and automatically adjust the temperature to maximize energy savings. They can also be controlled remotely via a smartphone app, allowing you to adjust the temperature before you arrive home. Many smart thermostats offer features like geofencing, which automatically adjusts the temperature based on your location.
- Smart Sensors: Detect occupancy and temperature fluctuations in different zones of your home, allowing you to fine-tune your cooling strategy. For example, you can set the air conditioner to focus on cooling occupied rooms while reducing cooling in unoccupied areas.
- Automated Controls: Integrate your air conditioner with other smart home devices, such as smart blinds or shades, to automatically adjust sun exposure and reduce heat gain.
By leveraging smart HVAC integration, you can create a more comfortable and energy-efficient home environment while minimizing energy waste.
Choosing the Right HVAC Contractor: A Crucial Step
Selecting a qualified and reputable HVAC contractor is essential for proper installation and maintenance of your air conditioner. A skilled technician can accurately assess your cooling needs, recommend the appropriate BTU rating and SEER rating, and ensure that the unit is installed correctly. A poorly installed air conditioner can negate many of the energy-saving benefits of a high-efficiency unit.
When choosing an HVAC contractor, look for:
- Licensing and Insurance: Ensure the contractor is properly licensed and insured.
- Experience and Expertise: Choose a contractor with a proven track record of installing and servicing air conditioners.
- References and Reviews: Check online reviews and ask for references from previous clients.
- Energy Efficiency Knowledge: Select a contractor who is knowledgeable about energy-efficient HVAC systems and can provide recommendations for maximizing energy savings.
- Transparent Pricing: Obtain a detailed written estimate that includes all costs associated with the installation or repair.
Don't hesitate to ask questions and compare bids from multiple contractors to ensure you're getting the best value for your money.
Conclusion: BTU and Beyond for a Sustainable Future
Understanding BTU is just the first step towards creating a more energy-efficient and comfortable home or business. By considering factors like SEER, EER, and smart HVAC integration, you can make informed decisions that will save you money, reduce your environmental impact, and improve your quality of life. Remember to consult with a qualified HVAC professional to ensure that you choose the right air conditioner for your specific needs. Investing in energy-efficient HVAC systems is not just a smart financial decision; it's an investment in a more sustainable future. The right BTU makes all the difference.