What Hvac Systems Qualify For Tax Credit
Imagine this: it's the peak of summer, the sun is blazing, and you walk into your home expecting a cool, refreshing blast of air conditioning. Instead, you're met with…nothing. Or worse, lukewarm air. A failing HVAC system can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you consider the potential expense. But before you panic and call a repair service, let's explore some simple troubleshooting steps you can take yourself, focusing on understanding which HVAC system upgrades might even qualify you for a valuable tax credit.
This guide is designed to empower you to diagnose common HVAC problems and attempt basic fixes safely. We'll also delve into the exciting world of energy efficiency and which HVAC systems might be eligible for tax credits, helping you save money both in the short and long term. Remember, safety is paramount. If at any point you feel uncomfortable or unsure, call a qualified HVAC professional immediately.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting: When Your AC Isn't Cooling
Let's start with the most common scenario: your air conditioner isn't cooling your home effectively.
Step 1: Check the Thermostat
This might seem obvious, but it's often the culprit. A simple thermostat setting error can leave you sweating.
- Is the thermostat set to "Cool"? Double-check that it's not accidentally set to "Heat" or "Off."
- Is the temperature set low enough? Make sure the desired temperature is significantly lower than the current room temperature.
- Is the fan set to "Auto" or "On"? "Auto" is generally more energy-efficient, as the fan only runs when the AC is actively cooling. If set to "On," the fan will run continuously, which might not always be necessary.
- Check the thermostat batteries. A dying battery can cause the thermostat to malfunction. Replace them with fresh batteries.
Step 2: Inspect the Air Filter
A dirty air filter is a major cause of poor AC performance. It restricts airflow, making your system work harder and less efficiently. This can also contribute to ice buildup on the evaporator coil, further reducing cooling capacity. Regular filter replacement is crucial for maintaining a healthy and efficient HVAC system.
- Locate the air filter. It's typically located in the indoor unit (furnace or air handler) or in a wall or ceiling vent.
- Inspect the filter. If it's visibly dirty or clogged with dust and debris, it needs to be replaced.
- Replace the filter. Use a filter with the correct size and MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) rating for your system. Check your owner's manual for recommendations. A higher MERV rating filters out more particles, but can also restrict airflow if it's too high for your system.
- How often should you replace the filter? This depends on factors like the type of filter, the air quality in your home, and whether you have pets. As a general rule, replace it every 1-3 months.
Step 3: Check the Outdoor Unit (Condenser)
The outdoor unit is responsible for releasing heat from your home. If it's blocked or obstructed, it can't do its job effectively.
- Ensure the area around the unit is clear. Remove any plants, shrubs, debris, or other obstructions that are within 2-3 feet of the unit.
- Check for ice buildup. If you see ice on the coils, turn off the AC and allow it to thaw completely. This could indicate a refrigerant leak or airflow problem. If ice buildup persists, call a professional.
- Clean the condenser fins. Over time, the fins can become clogged with dirt and debris. Use a garden hose with a gentle spray nozzle to clean them. Be careful not to bend the fins. You can also purchase fin combs specifically designed for cleaning condenser fins. Never use a pressure washer, as it can damage the unit.
Step 4: Check the Circuit Breaker
A tripped circuit breaker can cut power to your AC unit. This is a safety mechanism designed to prevent electrical overload.
- Locate your electrical panel.
- Identify the circuit breaker for your AC unit. It's usually labeled.
- Check if the breaker is tripped. A tripped breaker will be in the "Off" or "Middle" position.
- Reset the breaker. Flip the breaker to the "Off" position and then back to the "On" position.
- If the breaker trips again immediately, there's likely a more serious electrical problem. Do not repeatedly reset the breaker. Call a qualified electrician.
Step 5: Check the Vents
Make sure that vents are open and unobstructed to allow for proper airflow throughout your home.
- Ensure all vents are open. Don't block vents with furniture, rugs, or other objects.
- Inspect vents for obstructions. Check for dust, debris, or other blockages.
Troubleshooting: When Your Furnace Isn't Heating
Now, let's shift gears to address a common heating problem: your furnace isn't producing heat.
Step 1: Thermostat Checks (Again!)
Just like with cooling, the thermostat is often the first place to check.
- Ensure the thermostat is set to "Heat."
- Verify the temperature is set higher than the current room temperature.
- Check the thermostat batteries. Low batteries can cause malfunctions.
Step 2: Check the Gas Supply (If Applicable)
If you have a gas furnace, ensure the gas supply is turned on.
- Locate the gas shut-off valve. It's typically located near the furnace.
- Make sure the valve is in the "On" position. The valve should be parallel to the gas pipe.
- If you smell gas, immediately evacuate the premises and call your gas company or 911. Do not attempt to fix the problem yourself.
Step 3: Check the Pilot Light (If Applicable)
Some older furnaces have a pilot light that needs to be lit.
- Locate the pilot light access panel.
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions for lighting the pilot light.
- If the pilot light won't stay lit, the thermocouple might be faulty. This is a safety device that shuts off the gas supply if the pilot light goes out. Replacing a thermocouple should be done by a qualified technician.
Step 4: Check the Flame Sensor
Many modern furnaces have a flame sensor. If it's dirty, the furnace may shut down shortly after ignition.
- Locate the flame sensor. It's usually a small metal rod located near the burner.
- Turn off the furnace power at the breaker.
- Carefully remove the flame sensor.
- Clean the sensor with fine steel wool or sandpaper.
- Reinstall the sensor and restore power.
Step 5: The Blower Motor
The blower motor circulates air in the furnace. If it malfunctions, the furnace may overheat and shut down.
- Listen for unusual noises coming from the blower motor area.
- Check if the blower motor is running after the burners ignite.
- If the blower motor is not running or making strange noises, call a technician.
When to Call a Professional
While these troubleshooting steps can help you resolve many common HVAC problems, there are situations where it's best to call a qualified HVAC professional. Never attempt repairs involving refrigerant, gas lines, or complex electrical components. These repairs require specialized tools and knowledge and can be dangerous if performed incorrectly.
Call a professional if:
- You suspect a refrigerant leak.
- You smell gas.
- You are uncomfortable working with electricity or gas.
- The problem persists after attempting the troubleshooting steps outlined above.
- You need to repair or replace complex components like the compressor, evaporator coil, or heat exchanger.
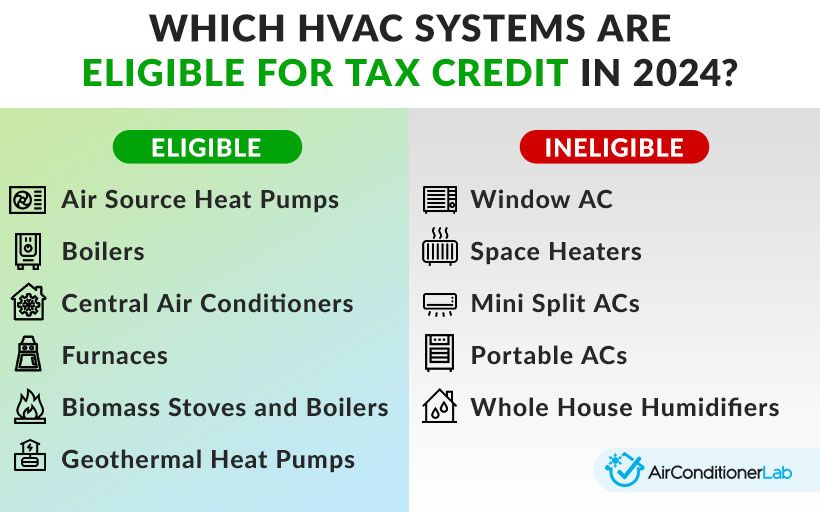
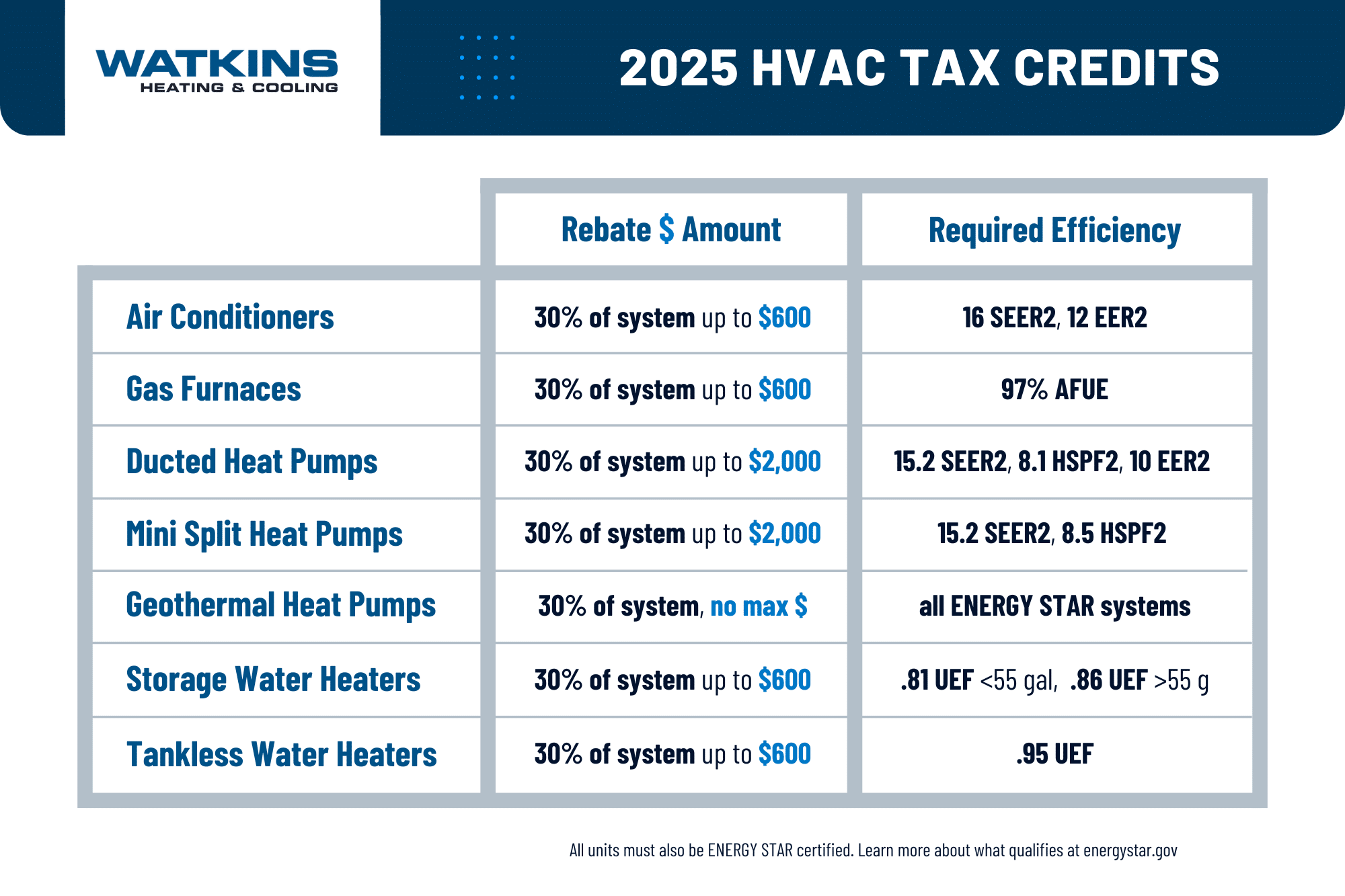
HVAC Systems That Qualify for Tax Credits
Now, let's talk about the exciting part: saving money through tax credits! The federal government, as well as some state and local governments, offer tax credits and rebates for installing energy-efficient HVAC systems.
Understanding Energy Efficiency Ratings
Before diving into the specifics, it's essential to understand the key energy efficiency ratings for HVAC systems:
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): This rating measures the cooling efficiency of air conditioners and heat pumps. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system.
- EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio): This rating measures the cooling efficiency of air conditioners at a specific operating condition.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): This rating measures the heating efficiency of heat pumps. The higher the HSPF rating, the more efficient the system.
- AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency): This rating measures the heating efficiency of furnaces. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficient the system.
Federal Tax Credits
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 significantly expanded and extended energy efficiency tax credits for homeowners. Here's a breakdown of the key provisions:
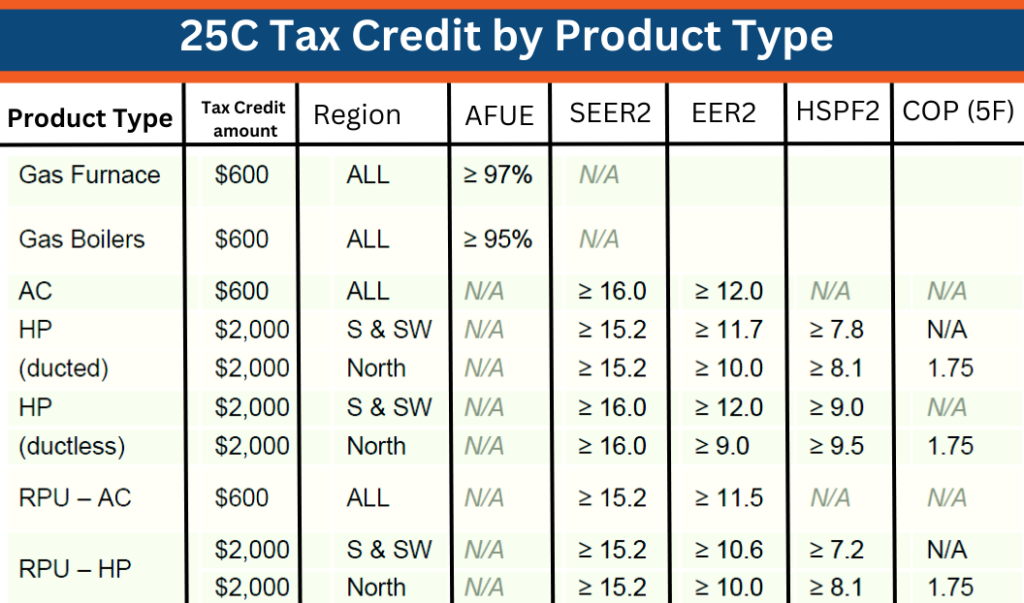
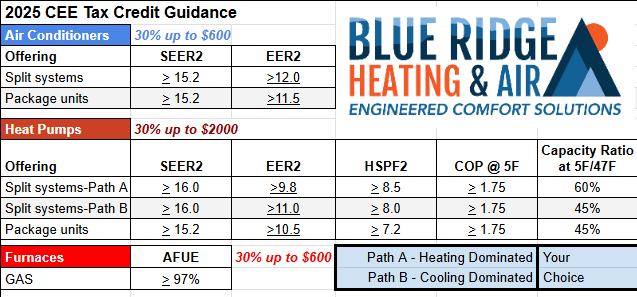
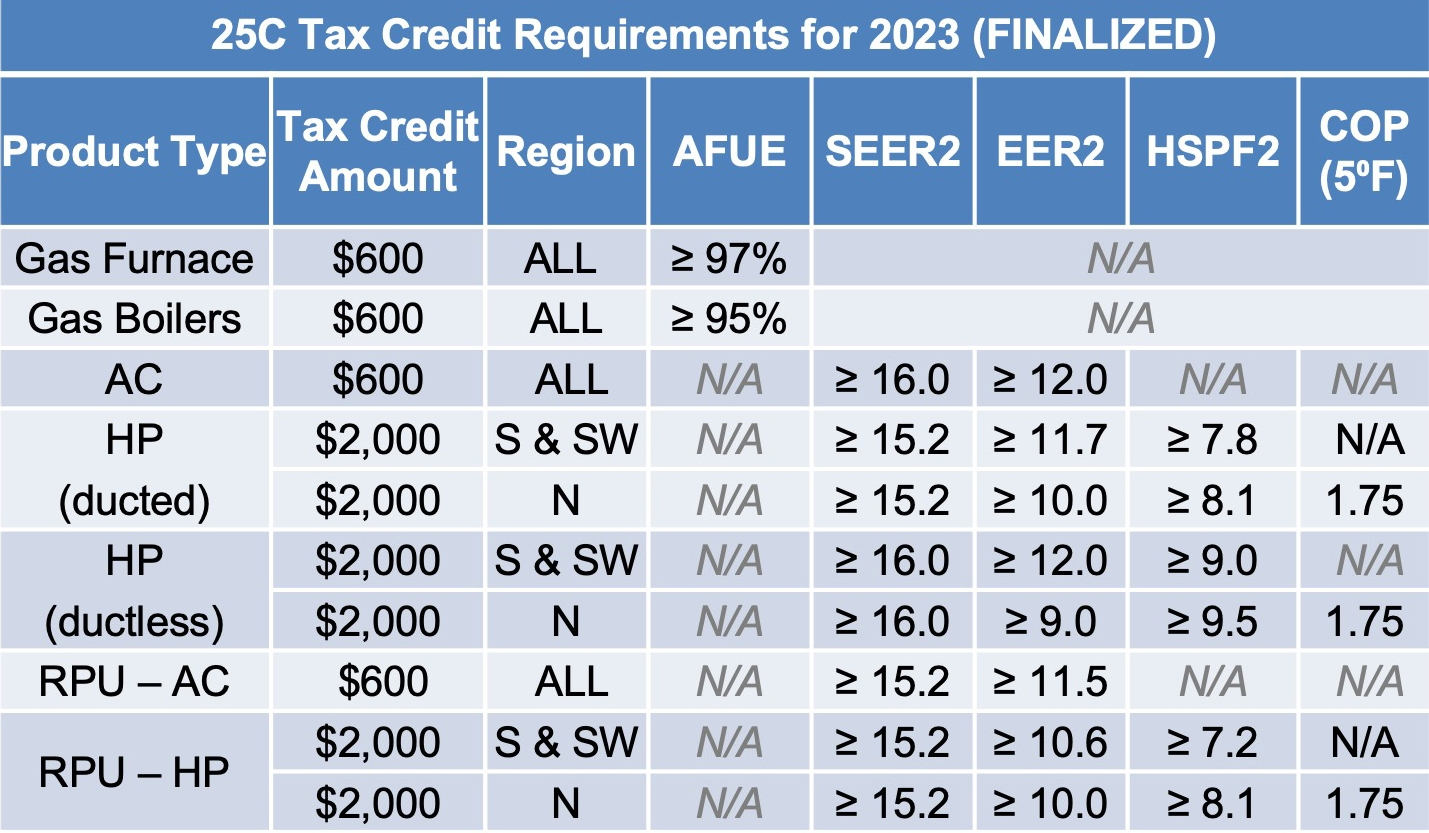
- Energy Efficiency Home Improvement Credit (25C): This credit provides a tax credit for 30% of qualified expenses, up to a maximum of $2,000 for qualifying HVAC equipment (and certain other energy-efficient home improvements). There are annual limits for specific items (e.g., $600 for qualified air conditioners, $600 for qualified furnaces, and $2,000 for heat pumps).
- New Energy Efficient Home Credit (45L): This credit is for builders of new energy-efficient homes that meet certain energy performance standards.
Qualifying HVAC Systems for the 25C Credit
To qualify for the 25C Energy Efficiency Home Improvement Credit, HVAC systems must meet specific efficiency standards set by the IRS. These standards may change over time, so it's important to consult the latest guidelines.
- Central Air Conditioners: Generally, to qualify, central air conditioners need to meet or exceed the highest efficiency tiers established by the Consortium for Energy Efficiency (CEE).
- Heat Pumps: Heat pumps must also meet certain CEE efficiency requirements. These requirements typically involve minimum SEER and HSPF ratings.
- Furnaces: High-efficiency furnaces with an AFUE of 95% or higher may qualify for the credit.
- Biomass Stoves and Boilers: Certain high-efficiency biomass stoves and boilers may also qualify.
How to Claim the Tax Credit
To claim the Energy Efficiency Home Improvement Credit, you'll need to:
- Purchase and install a qualifying HVAC system.
- Keep detailed records of your purchase, including receipts and model numbers.
- Obtain a Manufacturer's Certification Statement. This statement confirms that the product meets the energy efficiency requirements for the credit. Ask your contractor for this document.
- File IRS Form 5695 (Residential Energy Credits) with your tax return.
State and Local Incentives
In addition to federal tax credits, many states and local governments offer their own incentives for energy-efficient HVAC systems. These incentives can include rebates, tax credits, and low-interest loans.
- Check with your state energy office or local utility company to learn about available incentives in your area.
- The Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) is a valuable online resource for finding state and local incentives.
Important Considerations
- Consult with a qualified HVAC contractor. They can help you choose the right HVAC system for your needs and ensure that it's properly installed.
- Verify that the HVAC system meets the eligibility requirements for the tax credit before making a purchase.
- Keep accurate records of your purchase to support your tax credit claim.
- Consult with a tax professional to ensure that you are claiming the tax credit correctly.
By taking these steps, you can troubleshoot common HVAC problems, maintain your system's efficiency, and potentially save money through tax credits and rebates. Remember, safety is always the top priority. When in doubt, call a professional!