What Is A Split Unit Hvac

What is a Split Unit HVAC System? Your Questions Answered
Are you considering a new HVAC system or simply curious about the options available? You've likely heard the term "split unit" thrown around. This FAQ-style article will break down the essentials of split unit HVAC systems in a clear and easy-to-understand manner. We'll answer the most common questions homeowners and facility managers have, helping you make informed decisions about your heating and cooling needs.
Q1: What exactly *is* a split unit HVAC system?
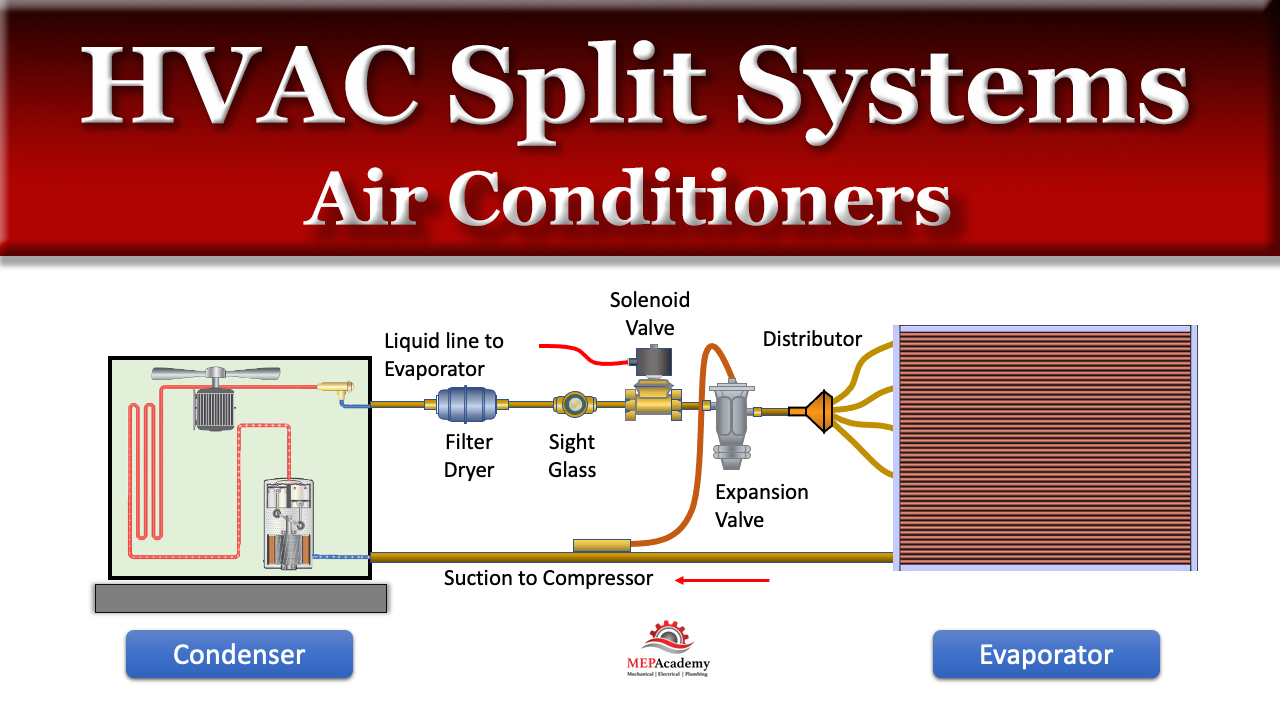
A split unit HVAC system, also known as a split system, is a type of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system that's divided into two main parts:
- Outdoor Unit: This part houses the compressor and condenser coil. It's usually located outside your home or building.
- Indoor Unit: This part contains the evaporator coil and a blower fan. It's typically installed inside your home or office, often in an attic, basement, or closet.
These two units are connected by refrigerant lines that circulate a special fluid called refrigerant. This refrigerant absorbs heat inside your home and releases it outside, or vice versa depending on whether you're heating or cooling.
Think of it as a system that separates the noisy, heat-generating components from the cooling/heating distribution, leading to quieter and often more efficient operation inside your living space.
Q2: How does a split unit HVAC system work in simple terms?
Imagine a simple process of heat transfer:
- Cooling Mode: In cooling mode, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air inside your home as it passes through the evaporator coil in the indoor unit. The blower fan then circulates this cooled air throughout your home. The heated refrigerant is then pumped to the outdoor unit, where the compressor increases its pressure and temperature. The condenser coil in the outdoor unit releases the heat into the outside air, converting the refrigerant back into a liquid. This liquid refrigerant then flows back to the indoor unit, completing the cycle.
- Heating Mode (Heat Pump): If your split unit is a heat pump, the process is reversed. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the outside air (yes, even in cold weather, there's still heat available) and releases it inside your home through the evaporator coil in the indoor unit. The refrigerant then travels to the outdoor unit, where the condenser coil releases cold air. In essence, it moves heat from one place to another, rather than generating heat directly.
The thermostat plays a crucial role in controlling the system, signaling when to turn on or off based on the desired temperature.
Q3: What are the benefits of choosing a split unit HVAC system over other types?
Split unit HVAC systems offer several advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Many split units are designed with energy-efficient components, potentially lowering your energy bills. Look for models with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings.
- Quiet Operation: By separating the noisy compressor and condenser to the outdoor unit, split systems offer significantly quieter operation inside your home compared to window units or packaged systems.
- Zoning Capabilities: Some split unit systems, especially those with multiple indoor units (multi-split systems), allow for zoning, meaning you can control the temperature in different areas of your home independently. This can further enhance energy efficiency and comfort.
- Space Saving: The compact indoor units can be mounted on walls or ceilings, saving valuable floor space.
- Improved Air Quality: Many split systems include air filters that help remove dust, pollen, and other allergens from the air, improving indoor air quality.
- Installation Flexibility: Split systems offer more flexibility in terms of installation location compared to ducted systems, as they don't require extensive ductwork.
While they have numerous benefits, it is important to consider the initial cost and the need for professional installation. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh these factors.
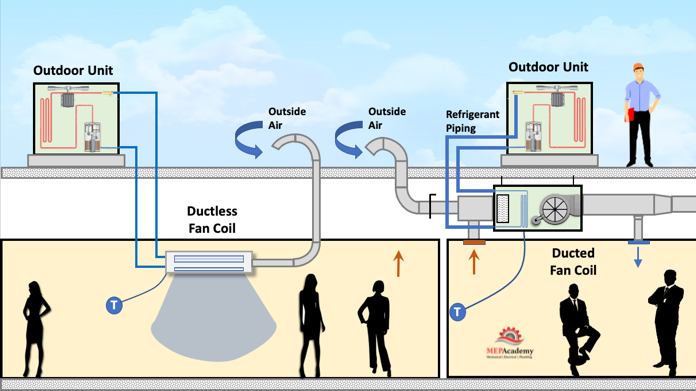
Q4: What's the difference between a single-split, multi-split, and mini-split system?
These terms relate to the number of indoor units connected to a single outdoor unit:
- Single-Split System: This is the most basic type, consisting of one outdoor unit connected to one indoor unit. It's suitable for cooling or heating a single room or a small area.
- Multi-Split System: This system connects one outdoor unit to multiple indoor units, allowing you to control the temperature in several rooms independently. Each indoor unit can be set to a different temperature, providing personalized comfort. These are often used in apartments or smaller office buildings.
- Mini-Split System: This is essentially a single-split or multi-split system, but the term often refers to smaller, ductless systems. They are called "mini" due to the compact size of the indoor units. They are very energy efficient and easy to install.
Choosing the right type depends on your specific needs and the number of areas you want to control independently. A multi-split system provides greater flexibility and energy savings through zoning.
Q5: How much maintenance does a split unit HVAC system require?
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of your split unit HVAC system. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace air filters regularly (usually every 1-3 months, depending on usage and filter type) to ensure proper airflow and air quality. Dirty filters can restrict airflow, reduce efficiency, and even damage the system.
- Coil Cleaning: Clean the evaporator and condenser coils at least once a year to remove dirt and debris that can impede heat transfer. You can use a fin comb to straighten bent fins.
- Refrigerant Level Check: Have a qualified technician check the refrigerant level periodically. Low refrigerant can indicate a leak and reduce the system's cooling or heating capacity.
- Drain Line Cleaning: Clean the condensate drain line to prevent clogs that can lead to water leaks and mold growth.
- Professional Inspection: Schedule an annual professional inspection to check for any potential problems and ensure the system is operating efficiently. A technician can identify and address issues before they become major repairs.
- Outdoor Unit Clearance: Ensure the outdoor unit is free from obstructions such as leaves, snow, or overgrown vegetation. This allows for proper airflow.
Following a regular maintenance schedule will help you avoid costly repairs and extend the lifespan of your system. Ignoring maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy bills, and premature system failure.
Q6: How do I choose the right size split unit HVAC system for my home or building?
Choosing the right size HVAC system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. An undersized system will struggle to cool or heat your space adequately, while an oversized system can cycle on and off too frequently, leading to wasted energy and uneven temperatures.
The size of an HVAC system is measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units). To determine the appropriate BTU rating for your needs, you need to consider several factors:
- Square Footage: The size of the area you need to cool or heat is a primary factor. A general rule of thumb is to use approximately 20 BTUs per square foot. However, this is just a rough estimate.
- Climate: The climate in your region plays a significant role. Hotter climates require larger systems.
- Insulation: The quality of your home's insulation affects how efficiently it retains heat or coolness. Well-insulated homes require smaller systems.
- Windows: The number and type of windows in your home can impact the heat gain or loss. Windows with low-E coatings help reduce heat transfer.
- Sun Exposure: The amount of direct sunlight your home receives can affect the cooling load.
- Number of Occupants: The number of people living in your home can also influence the cooling load.
- Appliance Heat: Heat-generating appliances such as stoves, ovens, and computers can contribute to the cooling load.
The best way to determine the appropriate size is to have a qualified HVAC technician perform a load calculation. This involves a thorough assessment of your home's specific characteristics to determine the exact heating and cooling requirements. They will consider all the factors mentioned above and use specialized software to calculate the precise BTU rating needed.
Avoid relying solely on the square footage rule of thumb. A professional load calculation will ensure you get the right size system for your needs, maximizing comfort and energy efficiency.
Q7: Can I install a split unit HVAC system myself, or do I need a professional?
While DIY projects can be tempting, installing a split unit HVAC system is generally not recommended for homeowners without specialized knowledge and experience.
Here's why professional installation is typically necessary:
- Refrigerant Handling: Handling refrigerant requires specialized tools and knowledge. Improper handling can be dangerous and can violate environmental regulations. Refrigerant leaks can harm the environment and can be costly to repair.
- Electrical Connections: Split unit systems require electrical connections that must be performed safely and correctly. Incorrect wiring can lead to electrical shocks, fires, or damage to the system.
- Proper System Setup: Correct installation involves more than just connecting the indoor and outdoor units. It also requires proper refrigerant charging, vacuuming the lines, and calibrating the system for optimal performance.
- Warranty Issues: Many manufacturers require professional installation for the warranty to be valid. DIY installation may void the warranty, leaving you responsible for any future repairs.
- Local Codes and Regulations: HVAC installations are often subject to local codes and regulations. A professional installer will be familiar with these requirements and ensure that the installation complies with all applicable rules.
- Specialized Tools and Equipment: Installing a split unit system requires specialized tools and equipment, such as a vacuum pump, refrigerant gauges, and a flaring tool.
Although it will cost more upfront, professional installation ensures that the system is installed safely, correctly, and in compliance with all applicable regulations. It also protects your warranty and helps to maximize the system's performance and lifespan. Consider professional installation as an investment in the long-term reliability and efficiency of your HVAC system.