What Is Heat Recovery Ventilation System

Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) is a type of mechanical ventilation system designed to improve indoor air quality while reducing energy consumption. It’s an increasingly popular solution for homes and buildings aiming for energy efficiency and a healthier living environment. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of HRV systems, explaining how they work, their benefits, and factors to consider when choosing one.
What is Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV)?
At its core, an HRV system is an engineered approach to controlled ventilation. Unlike simply opening windows or relying on natural air leakage, HRV systems provide a dedicated and efficient way to introduce fresh air into a building while exhausting stale air.
The key differentiator of HRV is its ability to recover heat from the outgoing stale air and use it to pre-heat (or pre-cool in warmer months) the incoming fresh air. This process minimizes the energy penalty associated with ventilation, making HRV systems an energy-efficient choice.
Think of it like this: imagine opening a window on a cold winter day. You get fresh air, but you also lose a lot of heat, forcing your heating system to work harder. An HRV system solves this problem by capturing much of that heat before it escapes and using it to warm the incoming fresh air, so you don't have to rely solely on your furnace.
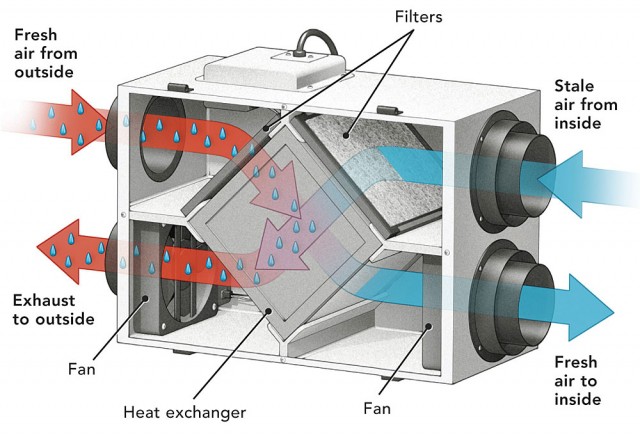
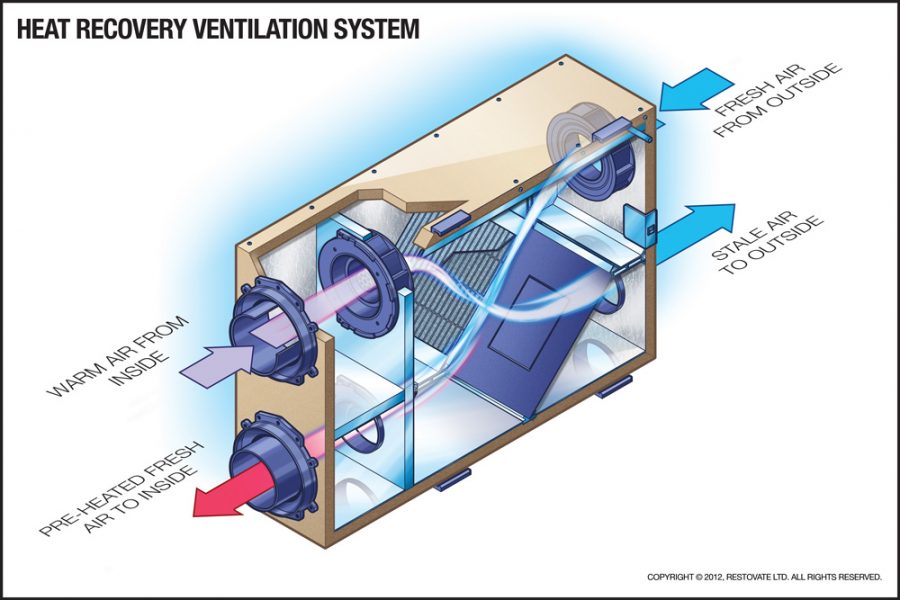
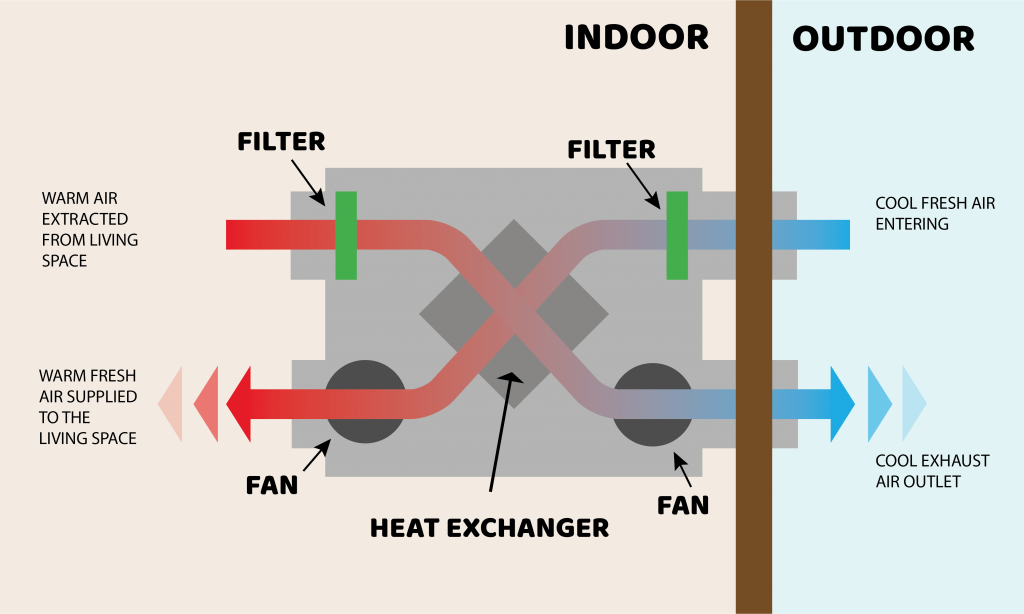
The Basic Components of an HRV System
An HRV system typically consists of the following key components:
- Fans: Two fans are used – one to extract stale air from inside the building and the other to draw fresh air from outside.
- Heat Exchanger Core: This is the heart of the system. It's a network of thin plates or channels that allow the outgoing and incoming air streams to pass close to each other without mixing. This allows heat to be transferred from one air stream to the other.
- Filters: Filters are used to remove dust, pollen, and other pollutants from both the incoming fresh air and the outgoing stale air. This helps improve indoor air quality.
- Ductwork: A network of ducts distributes fresh air throughout the building and collects stale air for exhaust.
- Controls: HRV systems often include controls that allow you to adjust the fan speed, operating mode, and other settings.
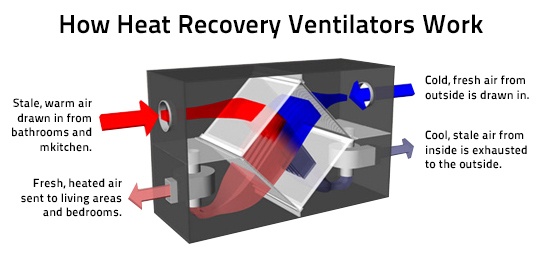
How Does HRV Work?
The operation of an HRV system can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Stale Air Extraction: The system draws stale, potentially polluted air from areas such as kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms, where moisture and odors tend to accumulate.
- Fresh Air Intake: At the same time, the system draws fresh air from outside. The intake vent is typically located away from potential sources of pollution, such as exhaust vents or garbage areas.
- Heat Exchange: The stale exhaust air and the fresh intake air pass through the heat exchanger core. As they pass, heat is transferred from the warmer air stream to the colder air stream. Crucially, the two air streams never mix, ensuring that pollutants from the stale air don't contaminate the fresh air.
- Air Distribution: The pre-heated (or pre-cooled) fresh air is then distributed throughout the living areas of the building, such as bedrooms and living rooms. The cooled stale air is exhausted outside.
- Filtration: Air filters clean both incoming and outgoing air.
Efficiency of Heat Recovery
The efficiency of an HRV system is measured by its sensible recovery efficiency (SRE). This indicates the percentage of heat that is recovered from the exhaust air and transferred to the incoming air. A higher SRE means greater energy savings. Modern HRV systems can achieve SRE values of 70% to 90% or even higher.
Benefits of Heat Recovery Ventilation
Investing in an HRV system offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: By constantly supplying fresh, filtered air and removing stale air, HRV systems help reduce the concentration of pollutants, allergens, and moisture indoors.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: By recovering heat from the exhaust air, HRV systems significantly reduce the energy needed to heat or cool the building, leading to lower utility bills.
- Moisture Control: HRV systems can help control humidity levels indoors, preventing problems such as mold growth and condensation, particularly in tightly sealed buildings.
- Odor Control: By removing stale air from kitchens, bathrooms, and other areas prone to odors, HRV systems help keep the indoor environment fresh and pleasant.
- Increased Comfort: HRV systems provide a consistent supply of fresh air, which can improve comfort levels, especially in tightly sealed buildings where natural ventilation is limited.
- Health Benefits: Improved indoor air quality can have significant health benefits, especially for individuals with allergies, asthma, or other respiratory conditions.
HRV vs. ERV: What's the Difference?
While HRV focuses primarily on heat recovery, Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) goes a step further by also recovering moisture. ERV systems are particularly useful in climates with high humidity levels, where they can help prevent excessive moisture buildup indoors. They may also be useful in dry climates by helping to retain some moisture.
Here's a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | HRV | ERV |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Recovery | Yes | Yes |
| Moisture Recovery | No | Yes |
| Best Climate | Cold, dry climates | Humid or very dry climates |
Choosing between HRV and ERV depends on your specific climate and needs. In general, HRV is a better choice for colder, drier climates, while ERV is more suitable for humid or very dry climates. Consult with a qualified HVAC professional to determine which system is best for your situation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an HRV System
Selecting the right HRV system for your home or building requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Building Size and Layout: The size and layout of your building will determine the required airflow rate and the number of supply and exhaust points needed.
- Climate: As mentioned earlier, the climate will influence whether an HRV or ERV system is more appropriate.
- Airflow Rate: The airflow rate (measured in cubic feet per minute, or CFM) should be sufficient to provide adequate ventilation for the building.
- Sensible Recovery Efficiency (SRE): Look for systems with a high SRE to maximize energy savings.
- Filtration: Choose a system with high-quality filters to remove dust, pollen, and other pollutants. Consider MERV ratings when evaluating filters. Higher MERV ratings indicate more effective filtration.
- Noise Level: Some HRV systems can be noisy, especially at higher fan speeds. Look for systems with low noise levels.
- Maintenance: Consider the ease of maintenance, such as filter replacement and cleaning of the heat exchanger core.
- Cost: The initial cost of an HRV system can be significant, but it's important to consider the long-term energy savings and improved indoor air quality.
- Installation: Proper installation is crucial for the performance of an HRV system. It's best to have the system installed by a qualified HVAC professional.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation is critical to ensure optimal performance of your HRV system. It is highly recommended to hire a qualified HVAC contractor with experience in HRV installation. The installer will determine the best location for the HRV unit, install the ductwork, and connect the system to the building's electrical system.
Regular maintenance is also essential to keep your HRV system running efficiently. This includes:
- Filter Replacement: Filters should be replaced regularly, typically every 3-6 months, depending on the filter type and air quality.
- Heat Exchanger Cleaning: The heat exchanger core should be cleaned periodically to remove dust and debris. This may involve removing the core and washing it with mild soap and water.
- Duct Cleaning: Ductwork should be inspected and cleaned periodically to remove dust and allergens.
- Inspection and Lubrication: Fans and other moving parts should be inspected and lubricated as needed.
Is an HRV System Right for You?
An HRV system can be a valuable investment for homeowners and building owners who are concerned about indoor air quality and energy efficiency. It is particularly well-suited for:
- New Construction: HRV systems are often incorporated into new building designs to meet energy efficiency standards and improve indoor air quality.
- Renovations: HRV systems can be retrofitted into existing buildings, although this may require more extensive ductwork modifications.
- Tightly Sealed Buildings: Buildings that are tightly sealed to improve energy efficiency can suffer from poor indoor air quality if they lack adequate ventilation. HRV systems provide a controlled and efficient way to ventilate these buildings.
- Homes with Allergies or Asthma: The improved indoor air quality provided by HRV systems can be particularly beneficial for individuals with allergies or asthma.
- Energy-Conscious Individuals: If you are committed to reducing your energy consumption and lowering your carbon footprint, an HRV system can be a worthwhile investment.
Before making a decision, it's important to assess your specific needs and consult with a qualified HVAC professional. They can help you determine the appropriate size and type of HRV system for your building and provide guidance on installation and maintenance.
In conclusion, Heat Recovery Ventilation is a sophisticated solution to deliver fresh air while conserving energy. It improves indoor air quality, reduces heating and cooling costs, and creates a healthier living environment. By understanding how HRV systems work and considering the factors outlined in this guide, you can make an informed decision about whether an HRV system is right for you.