What Is Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio

Imagine this: It's the peak of summer, the sun is beating down, and you walk into your home expecting a cool, refreshing blast of air. But instead, your air conditioner is wheezing, barely pushing out lukewarm air. Or worse, it's completely silent.
Before calling a costly repair technician, let's explore some basic troubleshooting steps you can safely perform yourself. We'll focus on identifying common problems and offering simple solutions. Remember, safety first! If at any point you feel uncomfortable or the problem seems complex, stop and call a qualified HVAC professional.
Understanding Your Air Conditioner and SEER
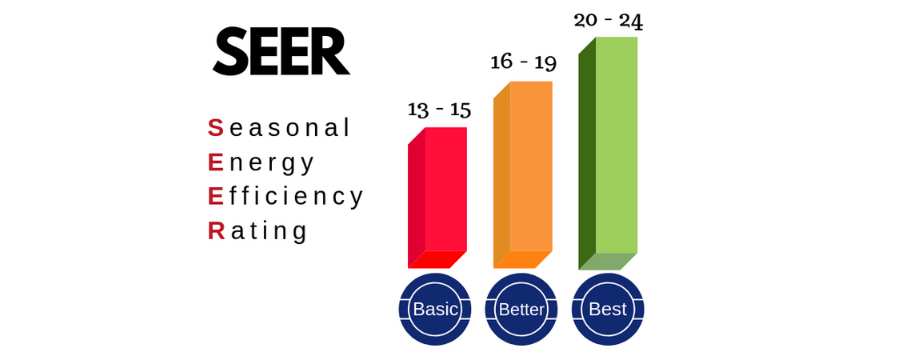
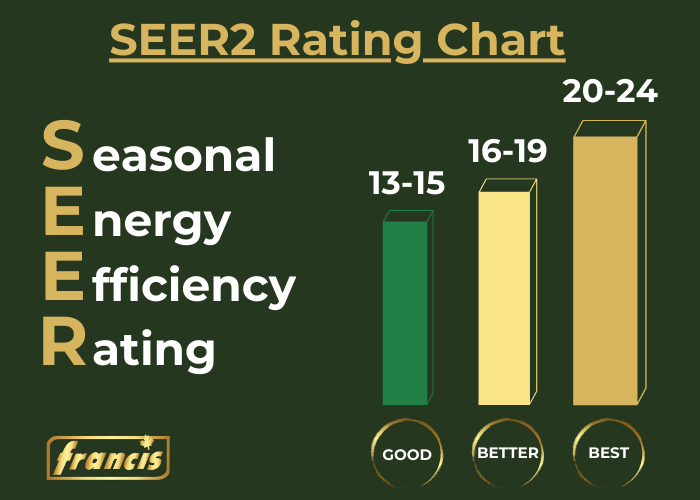
Before diving into troubleshooting, let’s briefly discuss the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER). This rating indicates how efficiently your air conditioner cools your home over an entire cooling season. A higher SEER rating means greater energy savings. Understanding your unit's SEER can help you assess its overall performance and efficiency.
SEER is calculated by dividing the total cooling output during a typical cooling season (in BTUs) by the total electrical energy input during the same period (in watt-hours). So, a unit with a SEER of 15 is more energy-efficient than one with a SEER of 13.
Factors that influence SEER:
- Unit Age: Older units typically have lower SEER ratings.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance ensures optimal efficiency.
- Installation Quality: Proper installation is crucial for achieving the rated SEER.
- Usage Patterns: How often and for how long you use your AC affects overall energy consumption.
Troubleshooting Your Air Conditioner: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's get your AC back up and running. Follow these steps in order, and remember to exercise caution when dealing with electricity.
Step 1: Check the Power Supply
This is the most basic, but often overlooked, step.
- Circuit Breaker: Locate the circuit breaker for your air conditioner in your home's electrical panel. Make sure it hasn't tripped. If it has, reset it. If it trips again immediately, do not keep resetting it. This indicates a more serious electrical problem that requires a professional electrician.
- Power Switch: Many air conditioners have a dedicated power switch near the outdoor unit. Ensure it's in the "On" position.
- Thermostat Batteries: If you have a digital thermostat, check the batteries. Weak or dead batteries can prevent the thermostat from communicating with the AC unit.
Step 2: Verify Thermostat Settings
Ensure your thermostat is correctly configured.
- Mode: Make sure the thermostat is set to "Cool" or "AC" mode, not "Heat" or "Fan Only."
- Temperature: Set the thermostat to a temperature significantly lower than the current room temperature. Give it some time (15-30 minutes) to see if the AC kicks in.
- Fan Setting: Try setting the fan to "Auto" instead of "On." In "Auto" mode, the fan only runs when the AC is actively cooling.
- Programming: Review your thermostat's programming schedule. Ensure there are no overrides or incorrect settings preventing the AC from running at the desired time.
Step 3: Inspect the Air Filter
A dirty air filter is one of the most common causes of AC problems.
- Location: The air filter is typically located in the indoor unit or in a wall or ceiling vent.
- Inspection: Remove the filter and hold it up to the light. If you can't see light through it, it's definitely dirty.
- Replacement: Replace the filter with a new one of the correct size and type. Refer to your AC unit's manual or the old filter for the correct specifications. This is a maintenance task you should perform regularly (every 1-3 months).
Step 4: Examine the Outdoor Unit (Condenser)
The outdoor unit plays a critical role in the cooling process.
- Clearance: Ensure the outdoor unit is free from obstructions. Remove any leaves, grass clippings, branches, or other debris that may be blocking airflow around the unit. Maintain at least 2-3 feet of clearance around the unit.
- Coil Cleaning: The condenser coils can become dirty over time, reducing the unit's efficiency. You can gently clean the coils with a garden hose. Turn off the power to the unit at the disconnect switch first! Spray the coils from the inside out, being careful not to bend the fins. If you are uncomfortable doing this, contact a professional.
- Fan Operation: Observe the fan on top of the outdoor unit. It should be spinning freely when the AC is running. If it's not, do not attempt to manually spin it. This could indicate a faulty motor or other mechanical problem requiring professional attention.
Step 5: Check the Indoor Unit (Evaporator)
The indoor unit is responsible for cooling the air inside your home.
- Frozen Coils: If you suspect the evaporator coils are frozen (little to no airflow from the vents), turn off the AC and set the fan to "On." This will help thaw the coils. A frozen coil is often caused by a dirty air filter, low refrigerant, or a malfunctioning blower motor. If the problem persists after thawing, it's best to call a professional.
- Condensate Drain Line: The condensate drain line removes moisture from the evaporator coil. A clogged drain line can cause water to back up and potentially damage your unit or home. Locate the drain line (usually a PVC pipe near the indoor unit) and check for any clogs. You can try clearing it with a wet/dry vacuum or by carefully inserting a stiff wire. If you are uncomfortable doing this, contact a professional.
When to Call a Professional
While the above steps can resolve many common AC problems, some issues require the expertise of a qualified HVAC technician. Never attempt to repair or replace components involving refrigerant, gas lines, or high-voltage electricity if you are not properly trained and certified.
Call a professional if you experience any of the following:
- Refrigerant Leaks: Refrigerant leaks are harmful to the environment and require specialized equipment and training to repair. Signs of a refrigerant leak include hissing noises, ice buildup on the coils, and poor cooling performance.
- Electrical Problems: If you suspect any electrical issues, such as burning smells, sparking wires, or a constantly tripping circuit breaker, immediately turn off the power to the unit and call an electrician or HVAC technician.
- Compressor Failure: The compressor is the heart of the AC unit. If it fails, the entire unit may need to be replaced. Compressor replacement requires specialized tools and knowledge.
- Gas Leaks (for Gas-Powered ACs): If you smell gas near your AC unit, immediately evacuate the area and call your gas company or a qualified HVAC technician. Gas leaks are extremely dangerous and can cause explosions or carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Unfamiliar Noises: Loud banging, grinding, or squealing noises from your AC unit can indicate serious mechanical problems. These noises should be investigated by a professional.
- Persistent Problems: If you've tried the troubleshooting steps above and your AC is still not working properly, it's time to call a professional.
Preventative Maintenance: Keeping Your AC Running Smoothly
The best way to avoid AC problems is to perform regular preventative maintenance. Here are some key steps:
- Regular Filter Changes: As mentioned earlier, change your air filter every 1-3 months, depending on usage and air quality.
- Coil Cleaning: Clean the outdoor condenser coils annually.
- Professional Tune-Ups: Schedule annual maintenance check-ups with a qualified HVAC technician. They can inspect and clean the unit, check refrigerant levels, and identify potential problems before they become major issues.
- Clearance Around Outdoor Unit: Maintain clear space around the outdoor unit, removing any obstructions.
- Monitor Performance: Pay attention to your AC's performance. If you notice any changes in cooling efficiency, unusual noises, or other issues, address them promptly.
Understanding SEER and Energy Savings
Upgrading to a newer AC unit with a higher SEER rating can result in significant energy savings over time. When considering a replacement, factor in the upfront cost of the new unit versus the potential long-term savings on your energy bills.
Here are some tips to maximize energy savings:
- Seal Air Leaks: Seal any air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent cool air from escaping.
- Use Ceiling Fans: Ceiling fans can help circulate air and make you feel cooler, allowing you to set your thermostat a few degrees higher.
- Close Curtains and Blinds: During the hottest part of the day, close curtains and blinds to block out sunlight and reduce heat gain.
- Install a Programmable Thermostat: A programmable thermostat allows you to automatically adjust the temperature when you're not home, saving energy.
By following these troubleshooting steps and preventative maintenance tips, you can keep your air conditioner running efficiently and comfortably for years to come. Remember, when in doubt, always consult with a qualified HVAC professional for assistance. Stay cool and safe!