What Should Be Humidity Level In Basement

Maintaining proper humidity levels in your basement is crucial for comfort, structural integrity, and indoor air quality. Too much moisture can lead to mold growth, wood rot, and musty odors, while too little humidity can cause dryness and discomfort. This article will delve into the ideal humidity range for basements, the factors that influence it, how to measure it, and strategies for achieving and maintaining optimal levels.
Understanding Basement Humidity
Humidity, or the amount of water vapor in the air, is typically measured as relative humidity (RH). This is the percentage of water vapor present in the air compared to the maximum amount the air could hold at a given temperature. Warmer air can hold more moisture than cooler air, which is why humidity levels often fluctuate throughout the day and year.
Basements are particularly susceptible to high humidity due to their location below ground level. The surrounding soil can be a significant source of moisture, which can seep into the basement through foundation walls and floors. Additionally, poor ventilation and inadequate waterproofing can exacerbate humidity problems.
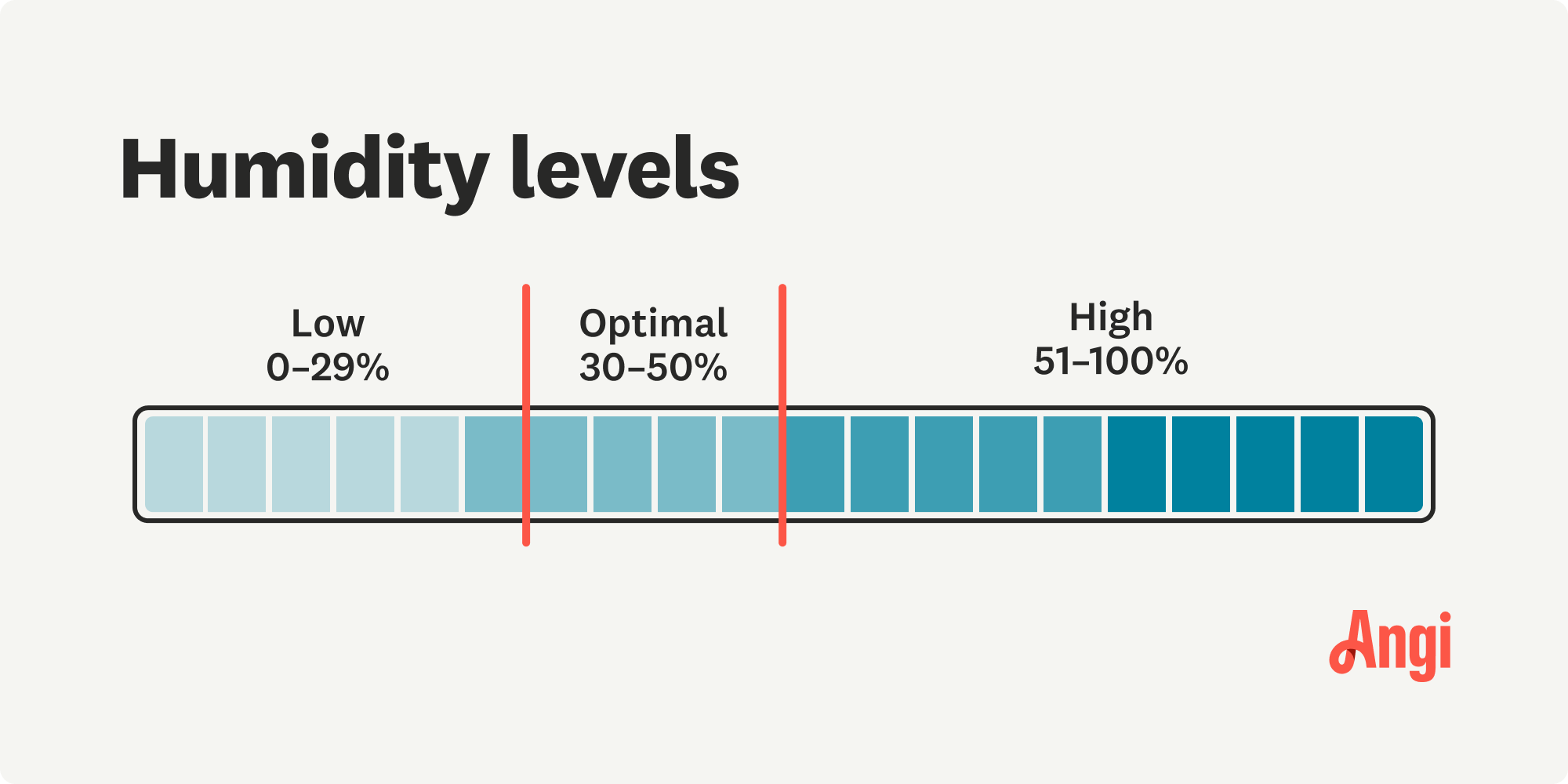
Ideal Humidity Range
The generally accepted ideal humidity range for basements is between 30% and 50% RH. Keeping humidity within this range helps prevent mold growth, control pests, and protect building materials.
- Below 30% RH: Air that is too dry can cause wood to shrink and crack, leading to structural damage. It can also exacerbate respiratory problems and dry out skin.
- Above 50% RH: High humidity creates a breeding ground for mold, mildew, and dust mites. It can also lead to condensation on surfaces, which can damage walls, floors, and stored items.
Strive to maintain humidity within the 30-50% range for a healthy and comfortable basement environment.
Factors Influencing Basement Humidity
Several factors can contribute to high or low humidity levels in your basement. Understanding these factors is essential for identifying and addressing humidity issues effectively.
External Factors
- Climate: Regions with high rainfall or high overall humidity will naturally have higher basement humidity levels.
- Soil Moisture: The moisture content of the soil surrounding the foundation directly impacts the amount of moisture that can seep into the basement. Poor drainage around the foundation can increase soil moisture.
- Groundwater Levels: High groundwater levels can lead to hydrostatic pressure against the foundation walls, forcing moisture into the basement.
Internal Factors
- Ventilation: Poor ventilation traps moisture inside the basement, leading to increased humidity levels.
- Leaks: Water leaks from plumbing, roof runoff, or foundation cracks can introduce significant amounts of moisture into the basement.
- Activities: Certain activities, such as showering, laundry, and cooking, can release moisture into the air and increase basement humidity levels.
- Foundation Type and Condition: Cracks, porous concrete, and lack of proper waterproofing can all contribute to moisture intrusion.
- HVAC System: An improperly sized or maintained HVAC system can contribute to humidity problems. An air conditioner that is too large will cycle on and off frequently, without running long enough to properly dehumidify the air.
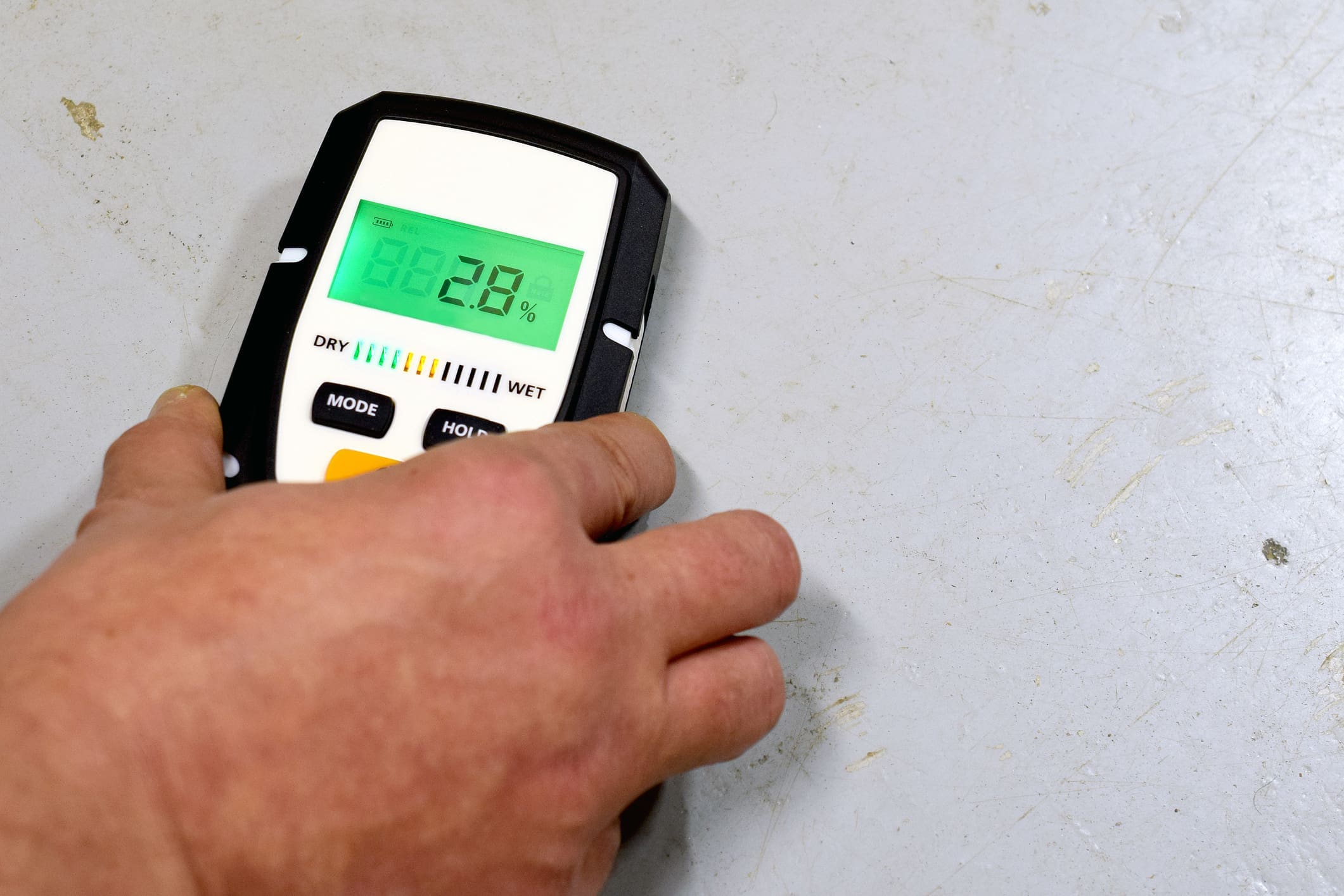
Measuring Basement Humidity
Regularly monitoring humidity levels in your basement is essential for identifying potential problems early on. The easiest and most affordable way to measure humidity is by using a hygrometer, also known as a humidity meter.
There are two main types of hygrometers:
- Analog Hygrometers: These hygrometers use a mechanical mechanism to measure humidity. They are generally less accurate than digital hygrometers.
- Digital Hygrometers: These hygrometers use electronic sensors to measure humidity. They are more accurate and often include additional features, such as temperature readings and data logging.
Place the hygrometer in a central location in the basement, away from direct sunlight and sources of heat or moisture. Monitor the humidity levels regularly, especially during periods of high humidity or heavy rainfall. Consider using multiple hygrometers in different areas of the basement to get a more comprehensive picture of humidity levels.
Strategies for Controlling Basement Humidity
Once you have identified the causes of high or low humidity in your basement, you can implement strategies to control it effectively. These strategies can be broadly categorized into moisture control, ventilation, and dehumidification/humidification.
Moisture Control
- Repair Leaks: Address any water leaks from plumbing, roof runoff, or foundation cracks immediately. This is the most crucial step in controlling basement humidity.
- Improve Drainage: Ensure that rainwater is directed away from the foundation with properly sloped landscaping and functioning gutters and downspouts. Consider installing a French drain to redirect groundwater away from the foundation.
- Waterproof Foundation: Apply a waterproof sealant to the exterior of the foundation walls to prevent moisture from seeping into the basement. This is often done during construction but can also be retrofitted. Interior waterproofing systems can also be installed to manage moisture intrusion.
- Seal Cracks: Seal any cracks in the foundation walls and floors with a waterproof sealant.
- Vapor Barrier: Install a vapor barrier on the basement floor and walls to prevent moisture from entering the space. Overlap seams and seal with tape to ensure that the barrier is airtight.
Ventilation
- Improve Air Circulation: Use fans to circulate air in the basement, especially in areas with poor ventilation.
- Open Windows (When Appropriate): During dry weather, open basement windows to allow fresh air to circulate. However, avoid opening windows during periods of high humidity, as this can worsen the problem.
- Install an Exhaust Fan: An exhaust fan can help remove moisture-laden air from the basement. Consider installing an exhaust fan in the laundry area or near a shower.
- Consider a Whole-House Ventilation System: For more comprehensive ventilation, consider installing a whole-house ventilation system, such as an energy recovery ventilator (ERV) or a heat recovery ventilator (HRV). These systems bring fresh air into the basement while exhausting stale air, helping to control humidity and improve indoor air quality. An HRV transfers heat; an ERV transfers both heat and moisture.
Dehumidification and Humidification
- Use a Dehumidifier: A dehumidifier removes moisture from the air, lowering humidity levels. Choose a dehumidifier that is appropriately sized for your basement. Consider a model with an automatic humidistat and continuous drainage.
- Consider a Whole-House Dehumidifier: For more consistent dehumidification throughout the entire home, consider installing a whole-house dehumidifier. These units are typically integrated into the HVAC system and can be controlled with a thermostat.
- Use a Humidifier (If Needed): In some cases, basement humidity levels may be too low, especially during the winter months. If this is the case, you may need to use a humidifier to add moisture to the air. This is less common than needing to dehumidify a basement.
Choosing the Right Dehumidifier
Selecting the right dehumidifier is important for effectively controlling basement humidity. Consider the following factors when choosing a dehumidifier:
- Capacity: Dehumidifier capacity is measured in pints of water removed per day. Choose a dehumidifier with a capacity that is appropriate for the size and humidity levels of your basement. A more humid basement will require a higher capacity dehumidifier.
- Coverage Area: Check the manufacturer's specifications for the recommended coverage area of the dehumidifier.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for a dehumidifier with an Energy Star rating to ensure energy efficiency.
- Features: Consider features such as an automatic humidistat, continuous drainage, and a timer.
- Noise Level: Dehumidifiers can be noisy, so consider the noise level when choosing a model, especially if the basement is used as a living space.
Professional HVAC Services
In some cases, controlling basement humidity may require professional assistance. An HVAC technician can help you identify the underlying causes of humidity problems and recommend appropriate solutions. They can also install and maintain dehumidifiers, ventilation systems, and other HVAC equipment.
Consider consulting an HVAC professional if you:
- Are unable to control basement humidity with basic measures.
- Suspect that your HVAC system is contributing to the problem.
- Are considering installing a whole-house dehumidifier or ventilation system.
- Have mold growth in your basement.
Costs Associated with Humidity Control
The cost of controlling basement humidity can vary depending on the strategies you implement. Simple measures, such as repairing leaks and improving drainage, may be relatively inexpensive. However, more extensive measures, such as waterproofing the foundation or installing a whole-house dehumidifier, can be more costly.
Here is a general overview of the costs associated with common humidity control measures:
- Hygrometer: $10-$50
- Dehumidifier: $150-$500 (depending on capacity and features)
- Foundation Crack Repair: $250-$800 per crack
- Foundation Waterproofing: $3-$10 per square foot
- French Drain Installation: $10-$30 per linear foot
- Whole-House Dehumidifier Installation: $1,500-$3,000
- HRV/ERV Installation: $2,000 - $4,000
While these costs may seem significant, they are often less than the cost of repairing damage caused by mold, wood rot, and other moisture-related problems. Moreover, controlling basement humidity can improve indoor air quality and overall comfort, making it a worthwhile investment.