What Should The Humidity Be In Your Home
Understanding Humidity and Your Home's Health
Maintaining the proper humidity level inside your home is crucial for comfort, health, and the preservation of your property. It's a delicate balance: too much humidity can lead to mold growth and respiratory issues, while too little can cause dry skin, irritated sinuses, and damage to wooden furniture. This article explores the ideal humidity range for your home, the problems associated with improper levels, and how to achieve and maintain that sweet spot using various HVAC solutions.
What is the Ideal Humidity Range?
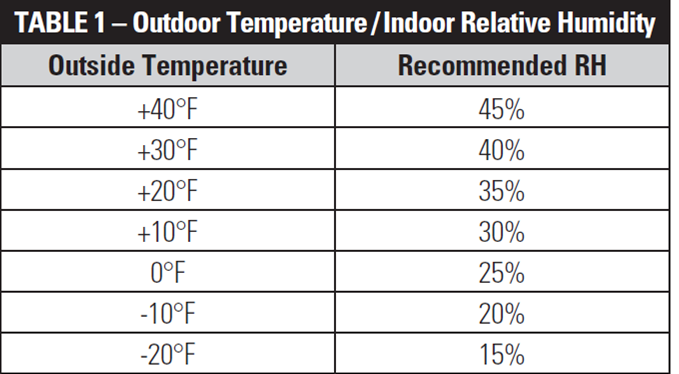
The generally recommended relative humidity (RH) level for indoor environments is between 30% and 50%. During the cooler months, aim for the lower end of this range (30-40%) to prevent condensation on windows and walls, which can lead to mold growth. In the warmer, more humid months, you can aim for the higher end (40-50%). Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air compared to the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at a specific temperature.
Think of it like this: a glass of water. At a certain point, the glass is "full," and any additional water spills over. Similarly, warm air can hold more moisture than cold air. When warm, humid air cools down, it can reach its "saturation point," leading to condensation.
Problems with High Humidity
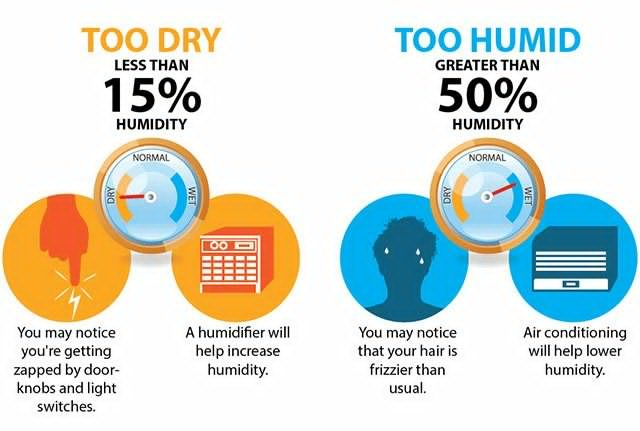
High humidity, typically above 60%, creates a breeding ground for mold, mildew, and dust mites. These allergens can trigger respiratory problems, including asthma and allergies. Additionally, excessive moisture can damage building materials like wood, drywall, and insulation, leading to costly repairs. You might notice musty odors, condensation on windows, and visible mold growth if humidity is too high.
For homeowners, this translates to increased doctor visits, potential structural damage, and a generally uncomfortable living environment. For facility managers, the stakes are even higher. Mold infestations in commercial buildings can lead to health code violations, lawsuits, and significant remediation costs.
Problems with Low Humidity
Low humidity, below 30%, can also be detrimental. It can cause dry skin, chapped lips, and irritated nasal passages, increasing susceptibility to colds and flu. Dry air can also damage wooden furniture, musical instruments, and artwork. Static electricity is another common symptom of low humidity.
From an HVAC technician's perspective, persistently low humidity can indicate leaks in the building envelope, inadequate ventilation, or a malfunctioning humidifier. Addressing these underlying issues is crucial for long-term comfort and building health.
Achieving and Maintaining Ideal Humidity Levels
Several methods can be used to control humidity levels in your home, ranging from simple lifestyle adjustments to sophisticated HVAC systems.
Dehumidifiers
Dehumidifiers remove excess moisture from the air. They are available in various sizes, from small portable units for individual rooms to whole-house systems integrated into your HVAC system. Portable dehumidifiers are a cost-effective solution for addressing localized humidity issues, but they require manual emptying of the water collection tank. Whole-house dehumidifiers offer more consistent humidity control throughout the entire home and typically drain automatically.
Cost: Portable dehumidifiers range from $100 to $400, while whole-house systems can cost $1,500 to $3,000 installed. Efficiency: Look for Energy Star-rated models for optimal energy efficiency. Lifespan: 5-10 years for portable units, 10-15 years for whole-house systems.
Humidifiers
Humidifiers add moisture to the air. They are particularly useful during the winter months when heating systems tend to dry out indoor air. Like dehumidifiers, humidifiers come in portable and whole-house versions. Portable humidifiers are suitable for smaller spaces, while whole-house humidifiers connect to your HVAC system and humidify the entire home. There are different types of humidifiers: evaporative, steam, and ultrasonic. Evaporative humidifiers use a wick or pad to evaporate water, while steam humidifiers boil water to create steam. Ultrasonic humidifiers use vibrations to create a fine mist.
Cost: Portable humidifiers range from $30 to $200, while whole-house systems can cost $500 to $1,500 installed. Efficiency: Evaporative humidifiers are generally the most energy-efficient. Lifespan: 1-3 years for portable units, 10-15 years for whole-house systems.
Air Conditioners
Air conditioners not only cool the air but also remove moisture as a byproduct of the cooling process. This can help to lower humidity levels in your home during the summer months. However, an oversized air conditioner that cycles on and off frequently may not effectively dehumidify the air. It's essential to choose the right size air conditioner for your home's square footage and climate.
SEER Rating: Look for air conditioners with a high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) for optimal energy efficiency. A higher SEER rating indicates that the unit uses less energy to cool your home. Cost: Air conditioners range from $3,000 to $7,000 installed, depending on the size and SEER rating. Lifespan: 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining healthy indoor air quality and controlling humidity levels. Ventilation systems bring fresh air into your home while exhausting stale, humid air. There are several types of ventilation systems, including exhaust fans, supply ventilation, and balanced ventilation.
Exhaust Fans: Exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens remove moisture and odors generated during showering and cooking. Supply Ventilation: Supply ventilation systems bring fresh air into your home through vents. Balanced Ventilation: Balanced ventilation systems, such as Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs) and Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs), exchange indoor and outdoor air while recovering heat or energy. HRVs are best suited for colder climates, while ERVs are more effective in humid climates.
Cost: Exhaust fans range from $50 to $300 installed, while HRVs and ERVs can cost $2,000 to $4,000 installed. Efficiency: HRVs and ERVs are highly energy-efficient, as they recover heat or energy from the exhaust air. Lifespan: 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to HVAC solutions, several lifestyle adjustments can help control humidity levels in your home:
- Take shorter, cooler showers.
- Use exhaust fans when showering or cooking.
- Fix any leaks in your plumbing.
- Dry clothes outdoors or use a clothes dryer with a vent to the outside.
- Ensure proper ventilation in crawl spaces and attics.
- Avoid overwatering houseplants.
Monitoring Humidity Levels
To effectively manage humidity in your home, it's essential to monitor humidity levels regularly. A hygrometer is a device that measures relative humidity. You can purchase a standalone hygrometer or a smart thermostat with built-in humidity sensing capabilities. Smart thermostats allow you to monitor humidity levels remotely and adjust your HVAC settings accordingly.
Cost: Hygrometers range from $10 to $50, while smart thermostats with humidity sensing can cost $150 to $300.
Working with HVAC Professionals
Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional is crucial for selecting and installing the right humidity control solutions for your home. An HVAC technician can assess your home's specific needs, recommend the most appropriate equipment, and ensure proper installation and maintenance. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning coils and changing filters, is essential for maintaining the efficiency and lifespan of your HVAC system. Don't hesitate to seek professional advice; it's an investment in your comfort, health, and the longevity of your home.
Remember that achieving and maintaining the ideal humidity level is an ongoing process. By understanding the factors that influence humidity and implementing the appropriate solutions, you can create a comfortable, healthy, and energy-efficient living environment.





.jpg?width=1754&name=Humidity level chart (1).jpg)