Where To Place Carbon Monoxide Detectors
Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Strategic Placement for Safety and Savings
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a silent killer. It's an odorless, colorless gas produced by incomplete combustion of fuels like natural gas, propane, wood, and heating oil. Properly placed carbon monoxide detectors are not just a safety precaution; they can contribute to energy savings by helping identify inefficient appliances that are producing excessive CO. Understanding where to install these devices is crucial for homeowners, business owners, and anyone looking to enhance their energy efficiency while ensuring a safe environment.
Why Accurate Placement Matters for Safety & Efficiency
Incorrectly positioned CO detectors might fail to alert you to dangerous levels of the gas. This defeats the purpose of having them. Furthermore, an improperly functioning or mislocated detector can trigger false alarms, leading to unnecessary evacuations and investigations. This disrupts your home or business and wastes energy (think about reopening doors and windows after a false alarm in winter). By optimizing detector placement, you improve their reliability and potentially uncover underlying appliance or HVAC system issues that contribute to energy waste. This aligns with the goals of homeowners trying to reduce energy bills and businesses adopting eco-friendly solutions.
Optimal Detector Placement: A Room-by-Room Guide
Follow these recommendations to maximize your CO detection effectiveness:
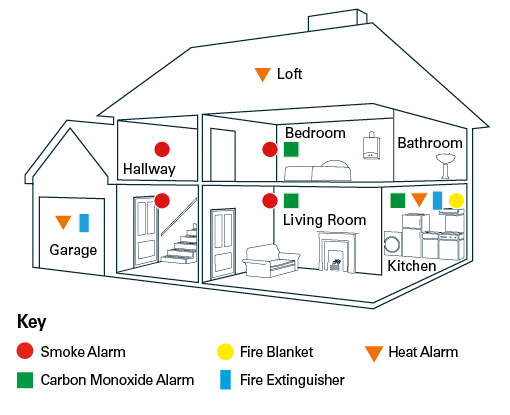
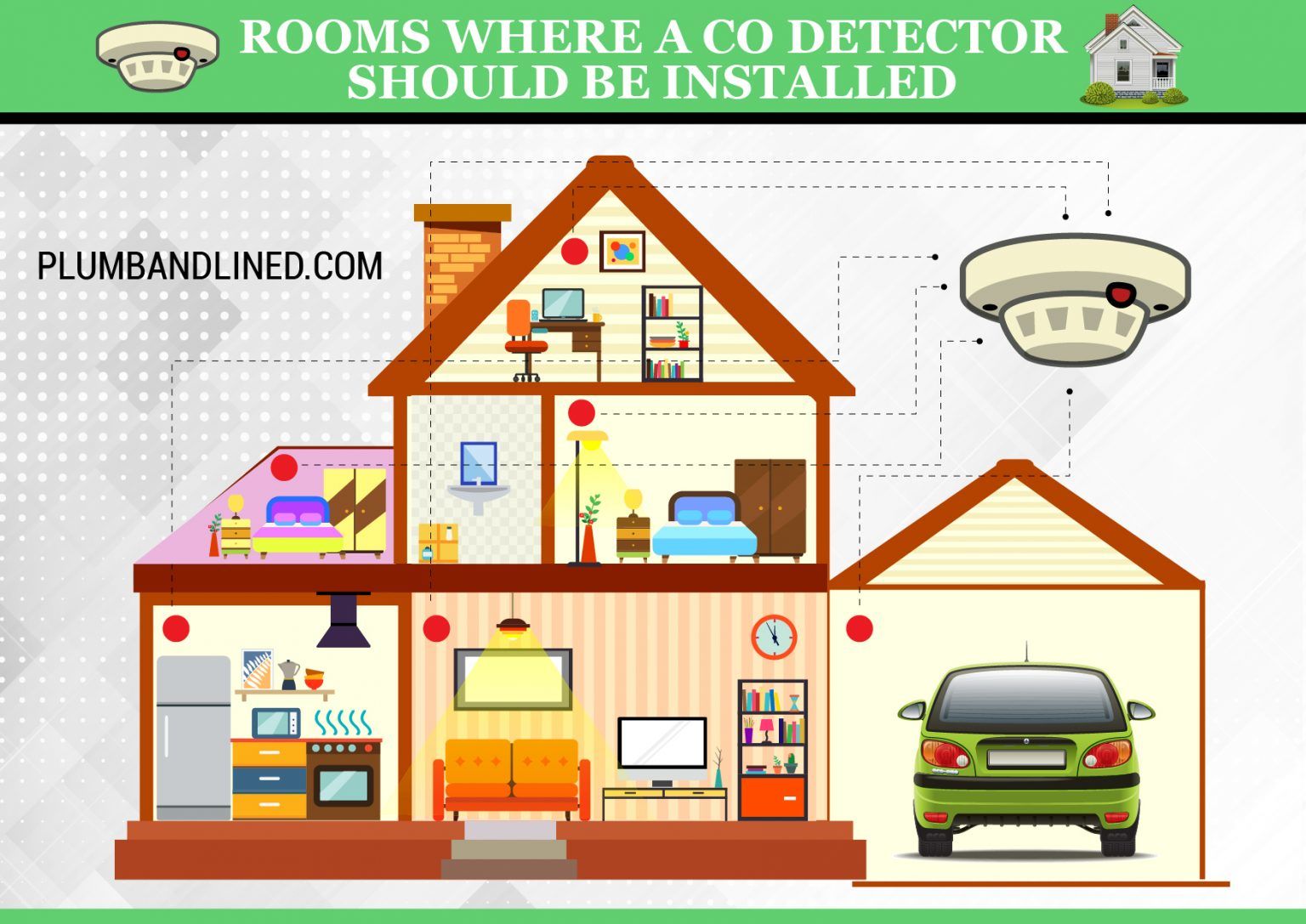
Essential Locations: Near Sleeping Areas
The Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Association (CPA) strongly recommends placing CO detectors near or outside sleeping areas. The goal is to wake you up if CO levels rise while you are asleep. Consider the following:
- Placement Height: Mount detectors on the wall, approximately 5 feet from the floor. This height ensures effective detection while minimizing accidental damage.
- Proximity to Bedrooms: Place detectors within 10 feet of each bedroom door. For larger homes, consider installing a detector inside each bedroom.
- Multi-Story Homes: Install a CO detector on every level, especially if bedrooms are located on multiple floors.
Why bedrooms? Most people spend a significant portion of their time asleep. Early detection is critical when individuals are unconscious.
Near Fuel-Burning Appliances
Any appliance that burns fuel can be a potential source of CO. This includes:
- Furnaces and Boilers: Place detectors within 10-20 feet of these appliances. A malfunctioning furnace can quickly produce dangerous CO levels.
- Water Heaters: Similarly, water heaters that use natural gas or propane should be monitored.
- Fireplaces: If you have a wood-burning or gas fireplace, install a detector in the same room. Ensure the flue is properly maintained and not blocked, as this is a common cause of CO buildup.
- Generators: Never operate a generator indoors or in an attached garage. Place a CO detector outside any door leading from a garage into the house.
- Gas Stoves/Ovens: While less common, gas stoves and ovens can also produce CO. Ensure proper ventilation and consider a detector in the kitchen.
Energy-Saving Tip: If your CO detector frequently alarms near a particular appliance, it could indicate inefficient combustion. Schedule a professional inspection to identify and address the problem. Often, simple maintenance like cleaning burners or adjusting gas pressure can improve efficiency and reduce CO production, leading to lower energy bills. Some utility companies offer rebates for energy-efficient appliance upgrades – check your local providers for options.
Special Considerations for Businesses
Commercial buildings have unique challenges for CO detection due to larger spaces and more complex HVAC systems. In addition to the above recommendations, consider:
- HVAC Systems: Install detectors near air intakes and returns to monitor for CO entering the building through the ventilation system.
- Parking Garages: Attached parking garages are a significant CO source. Install detectors near entrances and exits.
- Commercial Kitchens: Restaurants and other commercial kitchens with gas-powered appliances require robust CO monitoring.
LEED certification encourages using sensors to measure and control indoor air quality, including CO levels. Integrating CO detection with your Building Management System (BMS) can help optimize energy efficiency and maintain a healthy environment.
Locations to Avoid
Certain locations can hinder the performance of CO detectors and lead to false alarms or inaccurate readings:
- Near Windows and Doors: Drafts can dilute CO levels, preventing the detector from triggering in time.
- In Garages: Unless specifically designed for garage environments, regular car exhaust can trigger false alarms and shorten the detector's lifespan. Place detectors in attached garages, just outside the entry door to the house.
- High Humidity Areas: Bathrooms and laundry rooms can damage the sensor.
- Dusty or Dirty Environments: Dust and debris can clog the sensor, reducing its sensitivity.
- Direct Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can degrade the detector's components.
- Dead Air Spaces: Stagnant air in corners or behind furniture can prevent CO from reaching the detector.
Smart CO Detectors and HVAC Integration
Integrating smart CO detectors with your smart home system offers several benefits:
- Remote Monitoring: Receive alerts on your smartphone or tablet if CO levels rise, even when you're away from home.
- HVAC Shutdown: Some smart CO detectors can automatically shut down your HVAC system if CO is detected, preventing the gas from circulating throughout the building. This can be crucial in protecting occupants and allows for rapid response.
- Smart Thermostat Integration: Connect your CO detector to your smart thermostat for enhanced safety and energy efficiency. The thermostat can automatically adjust the temperature to minimize energy consumption during a CO event.
- Data Logging: Some smart detectors track CO levels over time, providing valuable insights into potential problems and allowing you to identify trends.
Consider devices compliant with Energy Star standards to ensure optimal energy use and performance. For example, if you have a smart thermostat like a Nest or Ecobee, many CO detectors can integrate to trigger an automatic shutdown of your gas furnace if CO is detected, preventing the spread of the hazard.
The ROI of Smart CO Detection
While smart CO detectors may have a higher initial cost, they offer significant benefits:
- Reduced Risk of CO Poisoning: The primary benefit is enhanced safety for your family or employees.
- Energy Savings: Integration with smart thermostats and HVAC systems can optimize energy use and prevent wasted energy during CO events.
- Reduced False Alarms: Advanced sensors and smart features can minimize false alarms, saving you time and money.
- Improved Home Value: A smart home system with integrated CO detection can increase your home's value and appeal to potential buyers.
Maintenance and Testing
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring your CO detectors function correctly:
- Test Regularly: Press the test button on each detector monthly to ensure it's working.
- Replace Batteries: Replace batteries annually, or as recommended by the manufacturer. Consider using long-life lithium batteries for extended protection.
- Vacuum Regularly: Gently vacuum the detector to remove dust and debris.
- Replace Detectors: CO detectors have a limited lifespan (typically 5-7 years). Check the manufacturer's instructions and replace detectors when they expire.
Important Note: Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for installation, maintenance, and testing of your CO detectors.
Local Codes and Regulations
Many municipalities have specific requirements for CO detector placement. Consult your local building codes and fire department to ensure compliance. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines often form the basis of these local regulations.
Beyond CO Detectors: Whole-House Energy Efficiency
While strategically placed CO detectors are essential for safety, they are just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to energy efficiency. Consider the following additional measures:
- Insulation: Proper insulation reduces heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, lowering your heating and cooling costs.
- Air Sealing: Seal any gaps or cracks in your home's envelope to prevent air leaks.
- Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors: Upgrade to energy-efficient windows and doors to reduce drafts and improve insulation.
- Smart Thermostats: Program your thermostat to automatically adjust the temperature based on your schedule.
- Regular HVAC Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for your HVAC system to ensure it's running efficiently.
By combining strategic CO detector placement with a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency, you can create a safe, comfortable, and cost-effective living or working environment. Consult with an HVAC professional or energy auditor to identify areas where you can improve your home's energy performance and potentially qualify for rebates or tax credits.