Why Does The Power Go Out During A Storm

Power outages during storms are a frustrating reality, affecting everything from our comfort to the operation of essential equipment. Understanding why these outages occur is crucial for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers alike. This article delves into the common causes of storm-related power outages and discusses their impact on HVAC systems.
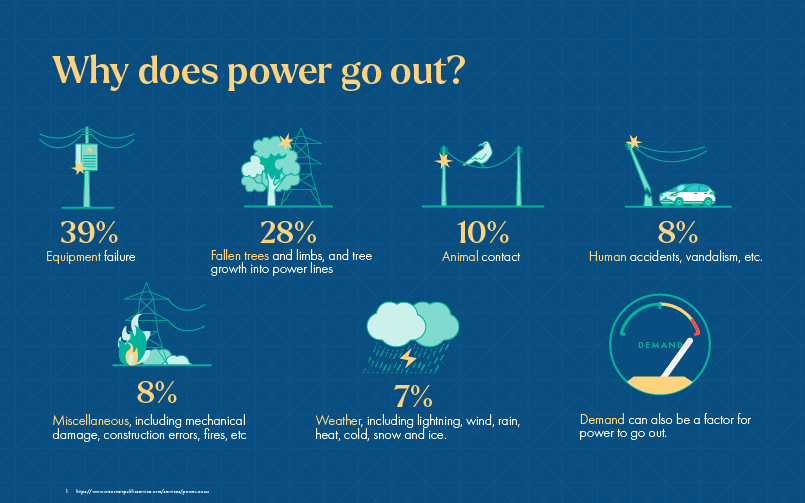
Common Causes of Storm-Related Power Outages
Direct Damage to Power Lines and Equipment
The most obvious cause is direct physical damage. High winds can topple trees, sending branches crashing into power lines. Ice storms add tremendous weight to lines and poles, causing them to snap. Lightning strikes, though less frequent, can directly hit and damage transformers and other grid components. For example, a large oak tree weakened by disease and saturated by heavy rain is far more likely to fall onto a power line than a healthy, well-maintained tree. After a major storm, you'll often see bucket trucks from utility companies repairing downed lines – a direct consequence of this kind of damage.
Indirect Damage and Cascading Failures
Sometimes, the damage is less direct but equally impactful. High winds can cause power lines to sway and touch, leading to short circuits and equipment failures. This can trigger a cascading effect, where one failure leads to another, impacting a wider area. Consider a scenario where a single downed line causes a voltage surge. This surge can travel down the line and damage transformers further down the grid, leading to multiple outages. This highlights the interconnected nature of the power grid.
Substation Issues
Substations are critical nodes in the power grid, responsible for stepping down high-voltage electricity for distribution to homes and businesses. They are vulnerable to flooding, high winds, and lightning strikes. A flooded substation can completely shut down power to a large area. Properly maintaining substations, including ensuring adequate drainage and lightning protection, is crucial for preventing outages.
Increased Demand During Storms
While not a direct cause of damage, increased demand can exacerbate existing problems. During heat waves preceding thunderstorms, air conditioners run continuously, putting a strain on the power grid. This increased load makes the grid more susceptible to failures when the storm hits. Power companies often issue conservation alerts during peak demand periods to help reduce the risk of outages.
Impact on HVAC Systems
Power outages can have significant consequences for HVAC systems, affecting their operation and potentially causing damage.
Complete System Shutdown
The most immediate impact is the complete shutdown of the HVAC system. Without electricity, the compressor, fans, and controls cannot function. This leads to a loss of heating or cooling, depending on the season. For homeowners, this means discomfort and potential safety concerns, especially for vulnerable populations like the elderly or those with medical conditions. For businesses, it can disrupt operations and lead to lost productivity.
Potential for Compressor Damage
Power surges that can occur during power restoration can damage the compressor, the heart of the cooling system. Compressors are designed to operate within a specific voltage range. A surge can overload the motor windings, leading to overheating and premature failure. Installing surge protectors can help mitigate this risk.
Refrigerant Leaks
While less common, sudden power outages can sometimes contribute to refrigerant leaks, especially in older systems with weakened seals or connections. The abrupt stop and start of the system can create pressure fluctuations that exacerbate existing weaknesses. Regularly inspecting and maintaining your HVAC system can help prevent these issues.
Thermostat Issues
Some thermostats, particularly older models, can lose their settings during a power outage. This can lead to the system operating inefficiently or not at all when power is restored. Programmable thermostats with battery backup can prevent this issue. Modern smart thermostats often reconnect to the network automatically after a power outage and retain their settings.
Protecting Your HVAC System During Storms
Taking proactive steps can help protect your HVAC system from the negative effects of power outages.
Surge Protection
Installing surge protectors is one of the most effective ways to safeguard your HVAC system. Surge protectors divert excess voltage away from sensitive components, preventing damage from power surges. Whole-house surge protectors offer the best protection, but individual surge protectors for HVAC units are also beneficial. The cost of a surge protector is minimal compared to the cost of repairing or replacing a damaged compressor. Look for surge protectors with a high joule rating.
Generators
A generator provides backup power during an outage, allowing your HVAC system to continue operating. There are two main types of generators: portable and standby. Portable generators are less expensive but require manual starting and refueling. Standby generators are permanently installed and automatically start when power is lost. Standby generators are more expensive but offer greater convenience and reliability. When selecting a generator, ensure it has sufficient capacity to power your HVAC system and other essential appliances.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
For critical applications, such as server rooms or medical facilities, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) provides immediate backup power to sensitive equipment. While typically used for electronic devices, a UPS can also be used to protect the control board and thermostat of an HVAC system, preventing data loss and ensuring continued operation during brief power interruptions. A UPS provides power instantly, unlike a generator which requires a short startup time.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for the overall health and longevity of your HVAC system. This includes inspecting and cleaning the system, checking refrigerant levels, and tightening electrical connections. A well-maintained system is less likely to be damaged by power fluctuations or other storm-related events. Schedule a professional HVAC inspection at least once a year.
Tree Trimming
If trees near your property pose a risk to power lines, consider having them trimmed or removed. This can significantly reduce the likelihood of a tree falling onto a power line and causing an outage. Consult with a certified arborist to ensure the trees are trimmed safely and properly.
Smart Thermostats with Power Outage Features
Consider upgrading to a smart thermostat that offers power outage features. Some smart thermostats can automatically adjust the temperature settings to conserve energy when power is restored, preventing the system from overloading. They can also send alerts to your smartphone when a power outage occurs and track the duration of the outage. These features can help you better manage your energy consumption and protect your HVAC system.
Understanding HVAC Efficiency and Costs
When considering backup power solutions, it's important to understand the efficiency ratings and costs associated with your HVAC system.
SEER Rating (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio)
The SEER rating measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner. A higher SEER rating indicates greater efficiency. Replacing an older, less efficient air conditioner with a newer, high-SEER model can significantly reduce your energy consumption and operating costs. For example, upgrading from a SEER 10 unit to a SEER 18 unit can reduce your cooling costs by nearly half. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term savings can be substantial.
HSPF Rating (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor)
The HSPF rating measures the heating efficiency of a heat pump. A higher HSPF rating indicates greater efficiency. Heat pumps are a more energy-efficient alternative to traditional furnaces in moderate climates. They can provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile option for homeowners. The HSPF rating helps you compare the heating efficiency of different heat pump models.
AFUE Rating (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency)
The AFUE rating measures the heating efficiency of a furnace. A higher AFUE rating indicates greater efficiency. Furnaces with an AFUE rating of 90% or higher are considered high-efficiency models. Upgrading to a high-efficiency furnace can significantly reduce your heating bills. Consider the climate you live in when choosing a furnace. In colder climates, a high-efficiency furnace can provide significant cost savings.
Cost Considerations
The cost of an HVAC system includes the initial purchase price, installation costs, and ongoing operating costs. When comparing different systems, consider the total cost of ownership over the lifespan of the equipment. Energy-efficient systems may have a higher initial cost but lower operating costs, resulting in long-term savings. Factors such as local climate, energy prices, and usage patterns can influence the total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
Power outages during storms are a common occurrence with the potential to significantly impact HVAC systems. Understanding the causes of these outages and taking proactive steps to protect your system is essential. By implementing surge protection, considering backup power solutions, and performing regular maintenance, you can minimize the risk of damage and ensure the continued operation of your HVAC system during severe weather events. Evaluating HVAC efficiency and costs can also help you make informed decisions about upgrading your system and reducing your energy consumption. Staying informed and prepared is the best defense against the disruptions caused by storm-related power outages.