Why Is My Heat Pump Not Blowing Warm Air

A heat pump is a highly efficient HVAC system that provides both heating and cooling. Unlike traditional furnaces that generate heat, heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another. In the winter, it extracts heat from the outside air and moves it indoors. When functioning correctly, your heat pump should keep your home comfortably warm, even on moderately cold days. However, if you find your heat pump blowing cold air, several issues might be at play. This article delves into the common causes of this problem, offering insights for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers alike.
Understanding How Heat Pumps Work
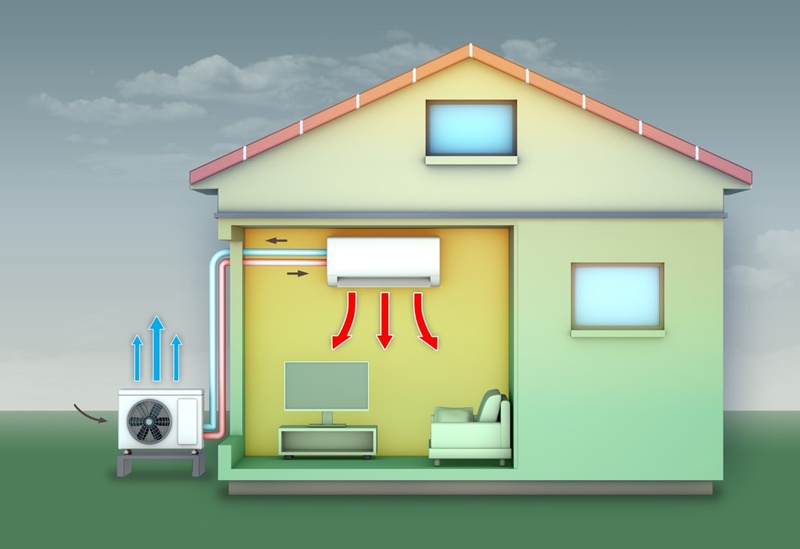
Before diagnosing why your heat pump is not blowing warm air, it's essential to understand its basic operation. A heat pump comprises two main components: an indoor unit (air handler) and an outdoor unit (condenser). These units are connected by refrigerant lines that circulate a special refrigerant. During the heating cycle, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the outside air (even on cold days, there's still heat available) and carries it indoors. The indoor unit then releases this heat into your home through vents.
The key to a heat pump's efficiency is its ability to reverse this process in the summer, acting like an air conditioner by moving heat from inside your home to the outside. This dual functionality makes it an energy-efficient and cost-effective solution for year-round comfort.
Common Causes of Cold Air from Your Heat Pump
Refrigerant Leaks
Refrigerant is the lifeblood of your heat pump. If there's a leak in the system, the refrigerant level will drop, reducing its ability to transfer heat effectively. A low refrigerant charge is one of the most frequent reasons a heat pump blows cold air. Detecting a refrigerant leak often requires specialized equipment and expertise. Look for signs such as ice buildup on the refrigerant lines or a hissing sound near the units. Technicians use electronic leak detectors or inject dye into the system to pinpoint the source of the leak. Repairing the leak and recharging the refrigerant to the correct level is crucial for restoring the heat pump's performance. According to the EPA, certified technicians are required for refrigerant handling due to environmental regulations.
Reversing Valve Problems
The reversing valve is a critical component that switches the direction of refrigerant flow, enabling the heat pump to switch between heating and cooling modes. If the reversing valve malfunctions or gets stuck, the heat pump may be stuck in cooling mode, even when you've set it to heating. A faulty reversing valve can sometimes be diagnosed by listening for a clicking sound as it attempts to switch positions. HVAC technicians use multimeters to test the valve's solenoid and wiring. Replacement of the reversing valve is often the best solution.
Frozen Outdoor Unit
During the heating cycle, the outdoor unit can accumulate frost, especially in cold and humid conditions. Heat pumps have a defrost cycle to melt this frost. This defrost cycle is normal. The heat pump may blow cool air for a short period (typically 5-15 minutes) while it's defrosting. If the outdoor unit is constantly frozen, it indicates a problem with the defrost cycle itself. Potential causes include a faulty defrost timer, defrost sensor, or a malfunctioning defrost relay. A clogged outdoor coil from leaves or debris can also restrict airflow and contribute to excessive ice buildup. Regular cleaning of the outdoor unit and ensuring proper airflow are essential preventative measures.
Dirty Air Filter
A dirty air filter restricts airflow to the indoor unit, reducing the amount of heat that can be transferred into your home. A clogged filter also forces the system to work harder, potentially leading to overheating and component failure. Regularly replacing your air filter (typically every 1-3 months) is one of the simplest and most effective ways to maintain your heat pump's performance and efficiency. Always use the filter type recommended by the manufacturer.
Ductwork Leaks
Leaky ductwork can result in significant heat loss, especially in unconditioned spaces like attics or crawl spaces. If your ductwork has leaks, the warm air produced by the heat pump can escape before it reaches your vents, resulting in cooler air being delivered to your rooms. Sealing ductwork with mastic sealant or foil tape can dramatically improve the efficiency of your heating system. Consider hiring a professional to perform a duct leakage test to identify and seal any leaks. According to Energy Star, properly sealed ducts can improve HVAC efficiency by as much as 20%.
Auxiliary Heat Activation Issues
Most heat pumps have an auxiliary heat (or emergency heat) setting, which activates electric resistance heaters to supplement the heat pump when it cannot keep up with the heating demand, particularly during extremely cold weather. If the auxiliary heat is not activating when it should, the heat pump may struggle to maintain the desired temperature, leading to the perception of blowing cold air. This could be due to a faulty thermostat setting, a malfunctioning auxiliary heat element, or wiring issues. Check your thermostat settings to ensure the auxiliary heat is enabled, and have a qualified technician inspect the auxiliary heat components.
Compressor Problems
The compressor is the heart of the heat pump, responsible for circulating the refrigerant throughout the system. A failing compressor can significantly reduce the heat pump's heating capacity. Common signs of a compressor problem include unusual noises, decreased heating performance, and increased energy consumption. Compressor failure often requires a complete replacement of the outdoor unit, which can be a significant expense.
Troubleshooting Steps for Homeowners
Before calling a professional, there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot the issue:
- Check the thermostat: Ensure the thermostat is set to "heat" mode and the temperature is set higher than the current room temperature. Verify that the fan is set to "auto" rather than "on."
- Inspect the air filter: Replace a dirty air filter with a clean one.
- Check the outdoor unit: Ensure the outdoor unit is free of debris, such as leaves, snow, or ice. Clear any obstructions that could be blocking airflow.
- Listen for unusual noises: Pay attention to any unusual noises coming from the indoor or outdoor unit. This information can be helpful for the HVAC technician.
- Observe the defrost cycle: Monitor the outdoor unit for the defrost cycle. If the unit is constantly frozen, it indicates a problem with the defrost system.
When to Call a Professional HVAC Technician
While some issues can be addressed by homeowners, many problems require the expertise of a qualified HVAC technician. It's best to call a professional when:
- You suspect a refrigerant leak.
- The reversing valve is malfunctioning.
- The defrost cycle is not working correctly.
- The auxiliary heat is not activating.
- You suspect a compressor problem.
- You are uncomfortable working with electrical components.
Heat Pump Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and lifespan of your heat pump. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Replace the air filter regularly: As mentioned earlier, this is one of the simplest and most effective maintenance tasks.
- Clean the outdoor unit: Remove any debris, such as leaves, grass clippings, and branches, from around the outdoor unit.
- Schedule annual professional maintenance: A qualified HVAC technician can inspect and clean the system, check refrigerant levels, and identify potential problems before they become major issues.
- Monitor system performance: Pay attention to any changes in heating or cooling performance and address them promptly.
Cost Considerations
The cost of repairing a heat pump that is blowing cold air can vary depending on the nature of the problem. Minor issues, such as replacing a dirty air filter, are relatively inexpensive. However, more complex repairs, such as repairing a refrigerant leak or replacing a compressor, can be costly. Regular maintenance can help prevent these costly repairs. A new heat pump installation can range from $4,000 to $12,000, depending on the size and efficiency of the system. High-efficiency models often qualify for rebates and tax credits, reducing the overall cost.
Conclusion
A heat pump blowing cold air can be frustrating, but understanding the potential causes can help you diagnose the problem and take appropriate action. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this article and seeking professional assistance when needed, you can ensure that your heat pump provides reliable and efficient heating and cooling for years to come. Remember that regular maintenance is key to preventing problems and maximizing the lifespan of your HVAC system. Consider a service agreement with a reputable HVAC company to ensure your system receives the attention it needs.